Murgab (Karakum)
|
Murgab Morghab, Murgap |
||
|
Murgab |
||
| Data | ||
| location |
Ghor , Faryab , Badghis ( Afghanistan ), Mary ( Turkmenistan ) |
|
| River system | Murgab | |
| Headwaters | in the Selseleh-ye Safīd Kūh Mountains 35 ° 2 ′ 42 ″ N , 65 ° 56 ′ 17 ″ E |
|
| Infiltration | in the Karakum Desert Coordinates: 38 ° 43 ′ 55 ″ N , 60 ° 37 ′ 40 ″ E 38 ° 43 ′ 55 ″ N , 60 ° 37 ′ 40 ″ E
|
|
| length | 978 km | |
| Catchment area | 46,880 km² | |
| Discharge at the gauge Qala-i-Niazkhan A Eo : 13,805 km² |
MQ 1966/1978 Mq 1966/1978 |
46.8 m³ / s 3.4 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the Bala Murghab A Eo gauge: 20,525 km² |
MQ 1969/1978 Mq 1969/1978 |
51.4 m³ / s 2.5 l / (s km²) |
| Discharge at the Takhta-Bazaar A Eo gauge : 34,700 km² Location: 486 km above the mouth |
MQ 1936/1985 Mq 1936/1985 |
48.7 m³ / s 1.4 l / (s km²) |
| Left tributaries | Kashan , Kushka | |
| Right tributaries | Abikaisor | |
| Big cities | Mary | |
| Medium-sized cities | Ýsolder | |
| Small towns | Murgap | |
|
Course of the Murgab in the southeast of Turkmenistan |
||
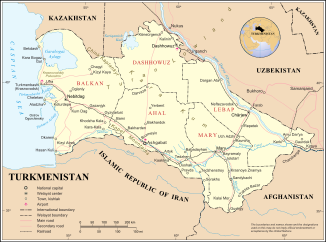
The Murgab (also Morghab, Turkmen Murgap ; Russian Мургаб ; in ancient times Margus or Greek Μάργος Margos ) is a 978 km long river in Afghanistan and Turkmenistan ( Central Asia ).
course
It rises in northwest Afghanistan in the Selseleh-ye Safīd Kūh Mountains (ancient name: Paropamisus ). Initially as a natural dividing line from Bandi-Turkestan in the north and the Selseleh-ye Safīd Kūh Mountains in the south, flowing in a valley to the west and then bending to the northwest, it reaches the city of Bala Murgab . From there it forms the natural border with Turkmenistan for around 16 km, after which it finally reaches the last-named state. There its water gradually enters the Karakum desert . In it it continues as an alien river towards the northwest, with the water of its largest tributary flowing in from the southwest - the Kuschka . Both rivers are dammed up at Daşköpri and Ýolöten by a barrier structure to form a reservoir ( ⊙ ). From now on, the running water is accompanied by railroad tracks to Mary . If it has enough water, its water seeps away as part of an inland delta that begins to split at Yolöten, only north of the Karakum Canal in the Karakum Desert.
Between the closely spaced cities Murgap and Mary the Murgab from Karakum and which is Trans Caspian railway crossing ( ⊙ ). Not far from the two cities are the ancient ruins of the oasis city of Merv .
Hydrometry
Average monthly discharge of the Murgab (in m³ / s) at the Bala Murghab gauge
from 1969–1978

history
The ruler of the Emirate of Bukhara , Ma'sum Shah Murad attacked Iran in 1788, captured Merw and destroyed the Murghab dams.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Article Murgab in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia (BSE) , 3rd edition 1969–1978 (Russian)
- ↑ Surface water resources in North Afghanistan ( Memento of the original from July 23, 2011 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b c Streamflow Characteristics at Streamgages in Northern Afghanistan and Selected Locations (PDF 5.6 MB) USGS.
- ↑ UNESCO - Bassin du Murghab - Station: Takhta-Bazar ( Memento of the original from March 3, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.