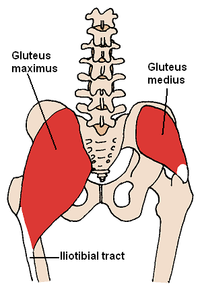
Gluteus medius muscle
| Gluteus medius muscle |
|---|
|
| large and central gluteal muscles |
| origin |
| Outer surface ( Facies glut (a) ea ) of the iliac bone ( Os ilium ), iliac crest ( Crista iliaca ) and its fascia ( Aponeurosis glut (a) ea ) |
| approach |
| large hillock ( greater trochanter ) of the thigh bone ( femur ) |
| function |
Human:
Animals: elongation |
| Innervation |
| Superior gluteus nerve |
| Spinal segments |
| L4-L5 |
The glut (a) eus medius muscle ( lat. For "middle gluteal muscle") is a skeletal muscle of the lower extremity , more precisely the rear ( dorsal ) layer of the rear hip muscles. It is almost completely covered by the gluteus maximus muscle .
course
The central gluteal muscle arises on the iliac bone ( os ilium ), more precisely on the outer surface ( facies glut (a) ea ) of the iliac blade ( ala ossis ilium ) between the two pelvic lines ( linea glut (a) ea anterior and linea glut (a) ea posterior ), from the iliac crest ( crista iliaca ) and its connective tissue covering ( fascia ) ( aponeurosis glut (a) ea ). The fibers unite and pull together like a cap to the large rolling hillock ( greater trochanter ) of the thighbone ( femur ).
A bursa ( Bursa trochanterica musculi glut (a) egg medii ) between the tendon and the greater trochanter decreases the friction.
function
The central gluteal muscle spreads the thigh to the side in the hip joint ( abduction ). When walking and running, it stabilizes the pelvis ( pelvis ) together with the small buttock muscle ( gluteus minimus muscle ) and prevents it from sinking to the side of the free leg .
The front part of the central gluteal muscle also turns the thigh inward ( internal rotation ) and bends it ( flexion ), while the rear part turns the thigh outward ( external rotation ) and stretches it ( extension ).
In quadruped mammals , it is the strongest of the hip muscles and the most important extensor of the hip joint. Due to this muscle action, it is largely responsible for the propulsion of the body. The twisting and spreading effect play practically no role.
paralysis
If the middle and small gluteal muscles are paralyzed at the same time, the so-called waddling gait occurs. H. With every step, the pelvis tilts to the side of the free leg ( Trendelenburg symbol ). A typical cause of such paralysis is intramuscular injections .