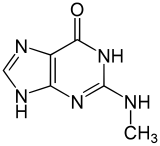
N 2 methylguanine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | N 2 methylguanine | ||||||||||||
| other names |
2-methylamino-3 H -purin-6-one |
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 7 N 5 O | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 165.15 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
N 2 -Methylguanine is a heterocyclic organic compound with a purine backbone. It is a derivative of the nucleobase guanine , whichis methylated at the amino group . It occurs as a component of the nucleoside N 2 -methylguanosine (m 2 G) in the RNA .
The dimethylated variant is N 2 , N 2 -dimethylguanine .
literature
- Douglas C. Youvan, John E. Hearst: "Reverse transcriptase pauses at N 2 -methylguanine during in vitro transcription of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA", in: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA , 1979 , 76 (8), pp. 3751-3754 ( PMC 383911 (free full text); PMID 91169 ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.