Nozaki-Hiyama-Kishi reaction
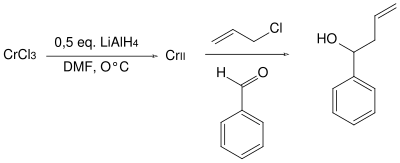
The Nozaki-Hiyama-Kishi reaction is a nickel- catalyzed chromium -mediated coupling reaction. In this case, from an aldehyde by reaction with allyl - or vinyl - halides formed a secondary allyl or vinyl alcohol. The reaction was first published by Tamejiro Hiyama and Hitoshi Nozaki in 1977. It is also named after Yoshito Kishi . A chromium (II) salt solution was reacted with benzaldehyde and allyl chloride.
If you compare this reaction with a Grignard reaction or the addition of lithium organyls , it is much more selective due to the relatively weaker nucleophilicity of the chromium organyl and functional groups such as ketones , esters , amides and nitriles are tolerated. However, the chromium organyl in the sense of HSAB is hard enough to enter into a 1,2-addition with α, β-unsaturated aldehydes. DMF and DMSO are used as solvents because they dissolve the chromium salts well.
Nickel (II) salts as a catalyst
In 1983 the same authors observed that vinyl halides, vinyl triflates and aryl halides react under similar conditions. In 1986 it was found that catalytic amounts of nickel (II) chloride accelerated the reaction.
Independently of this, Yoshito Kishi came to the same result in the same year as part of the palytoxin total synthesis.
Palladium acetate also showed good catalytic activity in this reaction.
Reaction mechanism
Nickel is first reduced to an element by the chromium (II), whereby the chromium is oxidized to the + III oxidation state. This is followed by an oxidative addition of nickel into the carbon-halogen bond to form a Grignard-like compound. After a transmetalation with chromium (III), a nucleophile is formed which can attack the aldehyde.
During the reaction, the amount of nickel catalyst must be kept low in order to avoid side reactions.
Similar reactions are for example the Grignard reaction (magnesium), the Barbier reaction (zinc) or reactions with organolithium reagents.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Y. Okude, S. Hirano, T. Hiyama, H. Nozaki: In Grignard type carbonyl addition of allyl Halides by Means of chromous salt. A chemospecific synthesis of homoallyl alcohols , in: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977 , 99 , 3179-3181.
- ↑ K. Takai, K. Kimura, T. Kuroda, T. Hiyama, H. Nozaki: Selective grignard-type carbonyl addition of alkenyl halides mediated by chromium (II) chloride , in: Tetrahedron Lett. 1983 , 24 , 5281-5284.
- ↑ K. Takai, M. Tagashira, T. Kuroda, K. Oshima, K. Utimoto, H. Nozaki: Reactions of alkenylchromium reagents prepared from alkenyl trifluoromethanesulfonates (triflates) with chromium (II) chloride under nickel catalysis , in: J. At the. Chem. Soc. 1986 , 108 , 6048-6050.
- ↑ H. Jin, J. Uenishi, WJ Christ, Y. Kishi: Catalytic effect of nickel (II) chloride and palladium (II) acetate on chromium (II) -mediated coupling reaction of iodo olefins with aldehydes , in: J. Am . Chem. Soc. 1986 , 108 , 5644-5646.
- ↑ K. Takai, K. Sakogawa, Y. Kataoka, K. Oshima, K. Utimoto: Preparation and Reaction of Alkenylchromium Reagents: 2-Hexyl-5-phenyl-1-penten-3-ol In: Organic Syntheses . 72, 1995, p. 180, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.072.0180 ; Coll. Vol. 9, 1998, pp. 472-477 ( PDF ).