OPC UA TSN
OPC UA over TSN ( known as OPC UA TSN until 2018 ) describes the combination of several technologies with which it is possible to transfer data in industrial production across manufacturers and in real time with a uniform, open standard. Industry experts consider OPC UA over TSN to be the communication protocol for Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things .
purpose
For communication within machines and between machines, proprietary communication protocols such as Profinet, EtherNet / IP, POWERLINK , EtherCAT, Profibus, Modbus or CAN have been used in industrial production . Interfaces or gateways are therefore necessary for communication between machines or components from different manufacturers.
The implementation of Industry 4.0 requires continuously networked production. This is difficult to implement with the current variety of protocols. A uniform communication standard is therefore necessary that enables continuous communication from the field level to the cloud . OPC UA over TSN is used by many automation and IT companies, including ABB, Bosch Rexroth , B&R Industrial Automation , CISCO , Hilscher, Hirschmann , Huawei , Intel , Kalycito, KUKA , Mitsubishi Electric , Molex , National Instruments (NI), Omron , Phoenix Contact , Pilz, Parker Hannifin, Rockwell Automation , Schneider Electric , Siemens , TTTech, Wago and Yokogawa have already been implemented in pilot products.
The technology
OPC UA over TSN is based on two main pillars:
- OPC UA is an industrial M2M communication protocol and data model that not only transports data, but can also describe it semantically.
-
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) refers to a number of sub-standards of the Ethernet standard IEEE 802 .1. The data transfer via standard Ethernet becomes real-time capable. The following substandards are relevant for industrial use:
- IEEE 802.1AS-Rev / D2.0: Timing and synchronization for time sensitive applications.
- IEEE 802.1CB: Frame Replication and Elimination for Reliability.
- IEEE 802.1Qbv: Enhancement for scheduled traffic
- IEEE 802.1Qci: Per-Stream Filtering and Policing
- IEEE 802.1Qcc: Stream Reservation Protocol (SRP) Enhancements and Performance Improvements
- IEEE 802.1Qbu: Frame preemtion
The TSN specifications are part of the general Ethernet specifications. Parts of the automotive industry rely on this standard. This means that the necessary semiconductor assemblies will probably be available quickly and comparatively inexpensively.
Necessary developments
In order to meet the requirements in industrial production, the OPC UA and Ethernet TSN technologies were (further) developed. The main focus was on the real-time capability of OPC UA. In order to be used for communication above the control level, the following requirements had to be met:
- Deterministic time behavior with a maximum jitter of less than 100 ns
- Cycle times of a maximum of 50 µs - 2 ms
In addition to the development of time-sensitive networking, it was necessary to expand OPC UA with a so-called publish / subscribe mechanism.
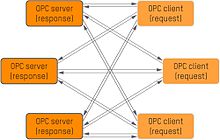
Until now, OPC UA only worked with a client / server mechanism . A client requests information (request) and receives a response from a server (response). This system reaches its limits when the network has many participants. The publish / subscribe model, on the other hand, enables one-to-many and many-to-many communication. A server sends its data to the network (publish) and every client can receive this data (subscribe). In combination with TSN, OPC UA with publish / subscribe meets the real-time requirements of the industry. This has now been confirmed in test beds by organizations such as the Industrial Internet Consortium or the LNI. A scientific white paper shows that OPC UA over TSN is 18x faster than all previously available Industrial Ethernet protocols.
The story of OPC UA over TSN
- January 2010 Adoption of the 802.1qav standard as the basis for audio / video applications ( AVB )
- November 2012: Expansion of the area of application and renaming from AVB to TSN
- November 2016: Foundation of the OPC UA TSN initiative at the invitation of the network specialist TTTech and the automation manufacturer B&R. The companies involved later became known as "Shapers".
- April 2017: Belden / Hirschmann and Phoenix Contact join the shapers
- November 2017: Pilz, Hilscher and Wago join the shapers
- April 2018: Rockwell Automation announces it has joined the Shapers
- November 2018: The OPC Foundation explains your entry into the field level with OPC UA over TSN.
- November 2018: ABB, Schneider and Rockwell join the board of the OPC Foundation
- November 2018: Presentation of the Steering Committee for OPC UA over TSN for the field level consisting of: ABB, BECKHOFF, Bosch-Rexroth, B&R, Cisco, Hilscher, Hirschmann, Huawei, Intel, Kalycito, KUKA, Mitsubishi Electric, Molex, Omron, Phoenix Contact, Pilz, Rockwell Automation, Schneider Electric, Siemens, TTTech, Wago, Yokogawa.
- November 2018: The first functional devices with OPC UA TSN are presented at the SPS IPC Drives (picture for B&R - photo by B&R booth)
organization
In November 2018, the OPC Foundation announced that it would expand the range of applications for OPC UA through the combination with TSN down to the field level. The work and vision of the shapers will be continued within the framework of the OPC Foundation. The companies ABB, Rockwell and Schneider-Electric were accepted into the board of the OPC Foundation. The OPC Foundation takes over the function of the user organization and will thus drive the further development and dissemination of OPC UA over TSN.
Web links
- OPC Foundation: official website
- Time-Sensitive Networking Task Group of the IEEE
- TSN testbed of the Industrial Internet Consortium
- OPC UA TSN A new Solution for Industrial Communication
Individual evidence
- ↑ Günter Herkommer: OPC UA - working group for real time founded. computer-automation.de, April 13, 2015, accessed January 30, 2017 .
- ↑ TSN - Time-Sensitive Networking. (No longer available online.) Autlook.at, November 2015, archived from the original on February 2, 2017 ; accessed on January 30, 2017 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Rockwell Automation joins the OPC UA Time-Sensitive-Networking Initiative. April 27, 2018. Retrieved April 27, 2018 .
- ↑ Shapers: Advancing OPC UA TSN: The road to interoperability. January 29, 2018, accessed January 30, 2018 .
- ↑ OPC UA TSN | Laying of the foundation stone for Industrial IoT and Industry 4.0. technik-medien.at, November 27, 2016, accessed January 30, 2017 .
- ↑ OPC Foundation: The OPC UA including TSN initiative announced by OPC Foundation November 5th has already been joined by many major industrial automation suppliers. November 27, 2018, accessed December 4, 2018 .
- ↑ IEEE 802.1 Working Group: IEEE802. Retrieved December 4, 2018 .
- ↑ TSN: Use in automobiles could significantly reduce costs. wirautomatisierer.de, July 16, 2016, accessed January 30, 2017 .
- ↑ Heike Henzmann: Real-time capability: OPC UA with TSN . No. 12 , 2015, p. 26–27 ( aktuelletechnik.ch [PDF; accessed on February 6, 2017]). aktuelletechnik.ch ( Memento of the original dated December 3, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Meinrad Happacher: From the sensor to the cloud. computer-automation.de, April 27, 2016, accessed January 30, 2017 .
- ^ Industrial Internet Consortium: Time Sensitive Networking (TSN). Retrieved December 4, 2018 .
- ↑ D. Bruckner, R. Blair, MP. Stanica, A. Ademaj, W. Skeffington, D. Kutscher, S. Schriegel, R. Wilmes, K. Wachswender, L. Leurs, M. Seewald, R. Hummen, EC. Liu, S. Ravikumar: OPC UA TSN. A new solution for industrial communication. (PDF) Retrieved December 4, 2018 .
- ↑ Smart Industry Forum: OPC UA TSN: A Small Step for Mankind, But a Giant Leap for Industry! Accessed December 5, 2018 .
- ↑ Rockwell Automation: Rockwell Automation Joins Industry Effort on OPC UA Time-Sensitive Networking. Accessed December 5, 2018 .
- ↑ a b OPC Foundation: OPC Foundation extends OPC UA including TSN down to field level. Accessed December 5, 2018 .
- ^ OPC Foundation: The OPC Foundation elects three new members to its Board of Directors. Accessed December 5, 2018 .
- ↑ OPC Foundation: Major Automation Industry Players join OPC UA including TSN initiative. Accessed December 5, 2018 .