Palaeoniscum
| Palaeoniscum | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
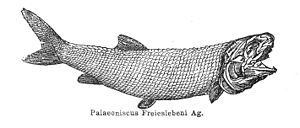
Palaeoniscum free life i |
||||||||||||
| Temporal occurrence | ||||||||||||
| 259 to 254 million years | ||||||||||||
| Locations | ||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Palaeoniscum | ||||||||||||
| Blainville , 1818 | ||||||||||||
Palaeoniscum is an extinct genus of the Actinopterygii subclass . This bony fish (Osteichthyes),belongingto the family of the Palaeoniscidae, lived in the Upper Permian ( Wuchiapingium ).
Initial description
Palaeoniscum was first described scientifically in 1818 by Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville . Type species of the genus is Palaeoniscum freilebeni .
Taxonomy
The genus Palaeoniscum forms with a very large number of be sister named after their family Palaeoniscidae within the order of Palaeonisciformes , including Acrorhabdus , Ambodipia , Apateolepis , Atherstonia , Canobius , cheirolepis , Coccocephalus , Cosmolepis , Cryphiolepis , Cycloptychius , Eurylepidoides , Eurylepis , Glaucolepis , Gonatodus , Guizhouniscus , Gyrolepis , Holurus , Howqualepis , Mesopoma , Myriolepis , Nematoptychius , Oxygnathus , Palaeoniscus , Phanerosteon , Progyrolepis , Pteronisculus , Rhadinichthys , Semionotus brodei , Trachelacanthus , Turfania , Turseodus , Wayaobulepis and Westollia . In addition to the type species Palaeoniscum freilebeni , the species Palaeoniscum blainvillei , Palaeoniscum comtus , Palaeoniscum elegans and Palaeoniscum vratislavensis are included. Synonyms are Eupalaeoniscus , Geomichthys , Palaeoniscus and Palaeothrissum . Above all, the name variant Palaeoniscus , introduced by Louis Agassiz in his revision and new description of the genus, was at times widespread and can still be found today.
features
Palaeoniscum had a torpedo-shaped body and was up to 30 centimeters long. Its caudal fin was heterocerk and very clearly notched. The dorsal fin was quite large. Both of these characteristics suggest a fast swimmer. Like other early ray fins , Palaeoniscum had mouth-connected air sacs that acted as primitive swim bladders . Its very sharp teeth grew back when lost , similar to today's sharks .
Way of life
Palaeoniscum was probably a very active, nectic and predatory carnivore.
Occurrence
Sites of Palaeoniscum can be found in:
Individual evidence
- ^ Robert Lynn Carroll : Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution . WH Freeman and Company, New York 1988, ISBN 0-7167-1822-7 .
- ^ Palmer, D .: The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals . Marshall Editions, London 1999, ISBN 1-84028-152-9 , pp. 36 .
