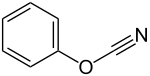
Phenyl cyanate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Phenyl cyanate | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
Phenyl cyanate |
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 5 NO | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, pungent smelling liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 119.12 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
74-75 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Phenyl cyanate is a chemical compound from the group of organic cyanates and a binding isomer to phenyl isocyanate .
properties
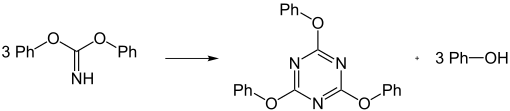
The liquid phenyl cyanate is relatively stable. Its tendency to trimerize to triphenyl cyanurate (see cyanuric acid ) is favored by Brønsted acids and bases, Lewis acids (see acid-base concepts ) and phenol .
presentation
The preparation of phenyl cyanate by nucleophilic substitution , i.e. the reaction between alkali metal phenolate and cyanogen halide (e.g. cyanogen bromide ), is only possible under special conditions. If cyanogen halide is reacted with an excess of alcoholate , iminocarbonic acid esters are initially obtained.
These also form trimerization products in the form of triphenyl cyanurates.
However, if the reaction mixture consisting of phenol and cyanogen halide is added dropwise, the phenolate ion is always present in a low concentration. Phenyl cyanate is preferably obtained, and the formation of iminocarbonic acid esters is suppressed.
Another possibility to prevent the trimerization is the thermal conversion of precursor compounds that keep the OCN group preformed. If thiocarbonic acid O -phenyl ester chloride is allowed to react with sodium azide to form 5-phenoxy-1,2,3,4-thiatriazole, this can be converted thermolytically to the desired product in good yield.
history
John Ulric Nef demonstrated the formation of iminocarbonic acid esters and cyanuric acid esters resulting from the reaction between alkali phenolate and cyanogen halide. This result could be reproduced independently of Nef, so that the cyanate esters supposedly obtained by other authors were considered refuted. The synthesis of cyanate esters from sterically hindered phenols was not successful until 1960. In 1964 Ernst Grigat and Rolf Pütter showed how cyanic acid esters can be obtained when phenolate is used as a reaction component in low concentration. In the same year, D. Martin succeeded in synthesizing phenyl cyanate by means of thermolytic conversion.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d D. Martin: Cyansäurephenylester. In: Angewandte Chemie. No. 76, 1964, p. 303.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ E. Grigat, R. Pütter: Chemie der Cyansäureester, I. Cyansäureester aus Hydroxylverbindungen and halogencyan. In: Chemical Reports. No. 97, 1964, p. 3013.
- ^ A b E. Grigat, R. Pütter: Chemie der Cyansäureester, I. Cyansäureester from Hydroxylverbindungen and halogencyan. In: Chemical Reports. No. 97, 1964, p. 3012.