Phleomycin D1
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
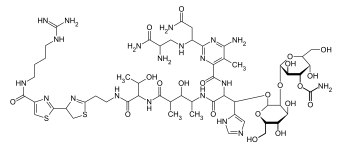
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Phleomycin D1 | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula |
|
|||||||||
| Brief description |
bluish powder (as a copper chelate complex) |
|||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 1427.52 g · mol -1 | |||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Phleomycin D1 is a copper chelating glycopeptide antibiotic . It is best known under the trade name Zeocin, which mainly contains phleomycin D1. It belongs to the bleomycin family and is also isolated from a mutant of Streptomyces verticillus . The mechanism of action is not yet fully understood, but Zeocin has a wide range of target organisms ( prokaryotes and eukaryotes ).
properties
The copper complex creates crystals with a bluish color. Phleomycin D1 loses its activity in the acidic and basic range as well as in the presence of oxidative reagents.
use
Phleomycin D1 is mainly used in molecular biology research. The big advantage is that B. not only works against bacteria or yeast, but against both. This enables the use of vectors for cloning experiments that are suitable for bacteria and yeast and so only one resistance gene is necessary for the selection .
Mode of action
The mode of action not yet fully understood. However, it is believed that phleomycin D1 penetrates the cell and intercalates the DNA . The metal ions (copper) then split the DNA. The cell's genetic material is damaged and it is no longer able to survive.
Mode of action of resistance
The resistance gene Sh ble enables the cell to express a 14 kDa protein which binds to phelomycin D1 in a highly specific manner. As a result, the antibiotic is inhibited and ineffective.
Web links
- Invivogen: Zeocin product sheet (PDF; 167 kB)
- Entry on Phleomycin D1 in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet Phleomycin from Streptomyces verticillus at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 12, 2017 ( PDF ).