Phosphoglucomutase
| Phosphoglucomutase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mass / length primary structure | 561 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer | |
| Cofactor | magnesium | |
| Isoforms | 2 | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name (s) | PGM1 , PGM2 , PGM3 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 5.4.2.2 , isomerase | |
| Response type | Rearrangement | |
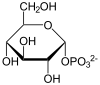
| Substrate | α- D -glucose-1-phosphate | |
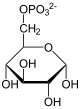
| Products | α- D -glucose-6-phosphate | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
Phosphoglucomutases (PGM) are enzymes that catalyze the shift of the phosphate residue in glucose phosphate from the 1- to 6-position and vice versa . Two classes are known: If the enzyme is specific for the α- anomer of glucose phosphates (see reactions below), it is called α-phosphoglucomutases ( αPGM ). In contrast, β-phosphoglucomutases only accept β- anomers (βPGM, EC 5.4.2.6 ).
Occurrence
α-phosphoglucomutases are common in prokaryotes and eukaryotes , β-phosphoglucomutase only in certain bacteria and protists .
meaning
These rearrangements are part of several metabolic pathways in all living things. Several genes are known in humans which code for different homologs , but of which only three have enzymatic activities: PGM1, PGM2 and PGM3. The latter is an acetylglucosamine phosphomutase ( EC 5.4.2.3 ). Mutations in the PGM1 or PGM2 gene can lead to PGM deficiency. Many genetic variants of PGM are known.
The PGM1 gene contains a plurality of hotspots of recombination , resulting in the plurality of variants explained. There is evidence that miscarriages can be traced back to some of these variants. The activity of PGM1 is increased by binding to and phosphorylation by Pak1 .
Catalyzed equilibrium
Glucose-1-phosphate is rearranged to glucose-6-phosphate and vice versa. The reactions are part of glycogen and starch breakdown , glycogen synthesis , uronic acid metabolism and galactose metabolism.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Dai, J. et al. (2006): Conformational cycling in beta-phosphoglucomutase catalysis: reorientation of the beta-D-glucose 1,6- (bis) phosphate intermediate . In: Biochemistry 45 (25); 7818-7824; PMID 16784233 ; doi : 10.1021 / bi060136v
- ↑ UniProt P36871
- ↑ Rana NA, Ebenezer ND, Webster AR, et al : Recombination hotspots and block structure of linkage disequilibrium in the human genome exemplified by detailed analysis of PGM1 on 1p31 . In: Hum. Mol. Genet. . 13, No. 24, December 2004, pp. 3089-102. doi : 10.1093 / hmg / ddh337 . PMID 15509594 .
- ↑ Gloria-Bottini F, Lucarini N, Palmarino R, et al : Phosphoglucomutase genetic polymorphism of newborns . In: Am. J. Hum. Biol . 13, No. 1, 2001, pp. 9-14. doi : 10.1002 / 1520-6300 (200101/02) 13: 1 <9 :: AID-AJHB1001> 3.0.CO; 2-1 . PMID 11466970 .
- ↑ Gururaj A, Barnes CJ, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R: Regulation of phosphoglucomutase 1 phosphorylation and activity by a signaling kinase . In: Oncogene . 23, No. 49, October 2004, pp. 8118-27. doi : 10.1038 / sj.onc.1207969 . PMID 15378030 .