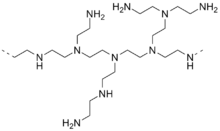
Polyethyleneimine
| Structural formula | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||
| General | ||||||||
| Surname | Polyethyleneimine | |||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||
| CAS number | 9002-98-6 | |||||||
| Monomer | Ethyleneimine | |||||||
| Molecular formula of the repeating unit | C 2 H 5 N | |||||||
| Molar mass of the repeating unit | 43.07 g mol −1 | |||||||
| properties | ||||||||
| Physical state |
viscous-liquid to solid |
|||||||
| solubility |
water soluble |
|||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||
|
||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||
Polyethyleneimine (abbr .: PEI) is formally the polymerisation product of its monomer ethyleneimine . If ethyleneimine is polymerized by ring-opening polymerization , however, a highly branched polymer molecule is formed . The amino groups are protonated when water is added and so it is present in aqueous solution as a strongly basic polycation .
Since it is a polymer, classification of the hazard class is only possible for a certain molar mass and for a certain composition (here the proportion of primary, secondary and tertiary amines). In general, the higher the molar mass (and in this specific case, the more secondary amine is present), the less irritating and harmful the product is.
Linear polyethyleneimine:
With methyl p- toluenesulfonate as initiator , 2-alkyl-substituted 2- oxazolines can be polymerized to give N-substituted polyethyleneimine. After saponification , a linear polyethyleneimine is formed from it.
use
Polyethyleneimine is u. a. used as a precipitating agent for the preparation of cell extracts. Due to its charge, it primarily precipitates the highly negatively charged nucleic acids , but possibly also strongly acidic proteins (have many negative charges in the form of carboxylate groups R – COO - on their surface). One can therefore use PEI to classify nucleic acids and proteins, especially because nucleic acids could interfere with other protein purification methods. High molecular weight PEI is used in papermaking as a flocculant and retention agent. It can also be used as an ion exchanger in water treatment.
Other possible uses are, for example, in the transfection of nucleic acids , such as. B. plasmids or siRNAs in human or murine cells, both for in vivo and in vitro transfections. The use of this synthetic polymer is also a cheap alternative to commercial transfection reagents .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Datasheet Polyethyleneimine, branched from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 9, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Blandine Brissaul et al: Synthesis of Linear Polyethyleneimine Derivatives for DNA Transfection. In: Bioconjugate Chem . 14, 2003, pp. 581-587.
- ↑ Jens Utecht, Martin Rübenacker, Claudia Nilz, Rainer Rahm: Insoluble Polymers which can swell only slightly with modified amino groups, process for their preparation, and their use. European Patent EP0925313, (online)
- ↑ M. Wirth, P. Fritsche, N. Stojanovic, M. Brandl, S. Jaeckel, RM Schmid, D. Saur, G. Schneider: A Simple and Cost-Effective Method to Transfect Small Interfering RNAs Into Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines Using Polyethyleneimines. In: pancreas. October 7, 2010 (Epub). PMID 20938367 .