Polyphosphides
Polyphosphides are polyphosphorus compounds in which the phosphorus atoms are present as anionic cage structures (so-called polyanions ). The compounds are extremely unstable and only stable and detectable at temperatures of liquid ammonia (−33.4 ° C to −77.4 ° C).
Manufacturing
Polyphosphides can be prepared from phosphane by deprotonation with gentle oxidation . The direct reaction of metals with white or red phosphorus at high temperatures and in the absence of air results in non-polymeric phosphides .
Known polyphosphides
| Some polyphosphides | |
|---|---|
![The structure of the [P7] 3− anion](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/ce/Metallphosphid_P3_7.svg/101px-Metallphosphid_P3_7.svg.png)
|
![The complex [P11] 3− anion](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/93/Metallphosphid_P3_11.svg/151px-Metallphosphid_P3_11.svg.png)
|
| P 7 3− | P 11 3− |
![[P14] 4− is made up of two bridged [P7] 3− cages](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/5b/Metallphosphid_P4_14.svg/151px-Metallphosphid_P4_14.svg.png)
|
![[P22] 4− is made up of two bridged [P11] 3− cages](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/37/Metallphosphid_P4_22.svg/151px-Metallphosphid_P4_22.svg.png)
|
| P 14 4− | P 22 4− |
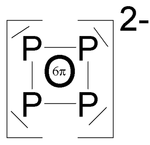
- P 4 2− has an aromatic character and is therefore a planar ring with a P − P − P bond angle of ~ 90 ° (example Cs 2 P 4 · 2 NH 3 , P − P bond lengths 215 pm ).
- P 5 -
- P 6 4−
- P 7 3− forms a cage structure with an equilateral P 3 triangle as a base, which is bridged by a trigonal P 4 pyramid as the "head". This structural element can also occur with higher homologues ([P 7 - ] )
- P 11 3−
- P 14 4− corresponds to a dimer of P 7 3− , with two of the "head" phosphorus atoms connected.
- P 16 2−
- P 19 3−
- P 21 3−
- P 30 N 5− The phosphide cage contains a central nitrogen atom from the solvent ammonia. The anion structure is present in the solid as a dimer.
- P 22 4− is made up of two bridged P 11 3− cages
Chemical properties
Polyphosphides can be converted into the corresponding hydrogen polyphosphides by gentle protonation in liquid ammonia . These thus represent the links to the polyphosphines . Chain-like polyphosphides are isoelectronic to the corresponding polysulfides and are similar in structure.
Web links
- Polyphosphides and hydrogen polyphosphides ( Memento from September 30, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 131 kB)
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c d e f A. F. Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , pp. 755-757.
- ^ H. Graf: Dissertation, University of Karlsruhe (TH), 1998.