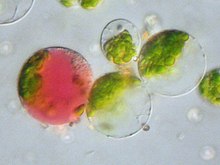
Protoplast
In cells with cell walls , the protoplast is the smallest independently viable morphological unit, ie the plasmatic content of a cell. This is why this term is used for bacteria , fungal and plant cells , as they can all have cell walls. Animal cells, on the other hand, have no cell wall and are only limited by their plasmalemma .
Protoplasts without a cell wall are produced by dissolving the cell wall with enzymes ( protoplast isolation ). In bacteria, the murein layer (cell wall) is dissolved by means of EDTA and lysozyme , in plant cells cellulose and pectin of the cell wall are dissolved by means of cellulases or pectinases . In the case of fungi with different types of cell walls, other means can be used accordingly, for example chitin cell walls can be dissolved with chitinase .
In the case of bacterial cells one speaks of, depending on the completeness of the removal of the cell wall
- Protoplasts (no murein present)
- Spheroplasts (Murein residues present)
The unit membrane / cytoplasmic membrane ( cell membrane ) is retained in any case. However, it is necessary to prepare and keep the protoplasts in an osmotically approximately isotonic medium, since otherwise they absorb water and burst in a hypotonic medium or are withdrawn from them in hypertonic water and thereby shrink.
use
Since protoplasts have no cell walls , they can easily take up DNA . Therefore, they are the starting material for the production of transgenic plants, in particular in those plants in which an Agrobacterium tumefaciens -mediated DNA transfer is not established. Protoplasts can also be fused with one another ( protoplast fusion ). In this way, two cells and thus two genomes can be fused together, even if the original organisms could not be crossed with one another; somatic hybrids arise . This technique is u. a. used in plant breeding . The protoplasts of vascular plants require the addition of phytohormones for the regeneration of whole plants. This regeneration usually takes place via an intermediate stage, the so-called callus . In contrast, the protoplasts of deciduous mosses such as z. B. Physcomitrella patens without adding phytohormones directly to the filamentous protonema . They behave like a germinating moss spore.
Individual evidence
- ↑ SC Bhatla, Justine Kießling, Ralf Reski (2002): Observation of polarity induction by cytochemical localization of phenylalkylamine-binding receptors in regenerating protoplasts of the moss Physcomitrella patens. Protoplasm 219, 99-105. doi: 10.1007 / s007090200010