Rambutyo
| Rambutyo | ||
|---|---|---|
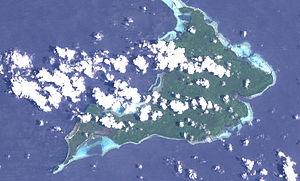
| NASA satellite image of Rambutyo | ||
| Waters | Bismarcksee | |
| Archipelago | Admiralty Islands | |
| Geographical location | 2 ° 18 ′ S , 147 ° 49 ′ E | |
|
|
||
| length | 17 km | |
| width | 8 kilometers | |
| surface | 88 km² | |
| Highest elevation | 306 m | |
| Residents | 1000 11 inhabitants / km² |
|
| main place | Lenkau | |
| Admiralty Islands with Manus and Rambutyo | ||
Rambutyo (German also: Jesus-Maria-Insel) is an island in the north of Papua New Guinea and belongs to the province of Manus .
geography
With an area of around 88 km², Rambutyo is the second largest island in the group of Admiralty Islands after Manus . Rambutyo is located 41 km southeast of Manus and south of the islands of Tong and Pak . The population of around 1000 is mainly distributed in the two places Lenkau and Penchal in the west. The forested island is of volcanic origin and reaches a height of 306 meters, according to older information only 216 meters. Together with the islands of Patuam, Malai and Bundro to the north, Rambutyo forms a group of islands known as the Horno Islands. On Rambutyo and the surrounding islands they speak Titan, Lenkau and Penchal. Rambutyo can only be reached by boat; the island has no airfield.
On Manus, Rambutyo Island and Lou is Meek's Pygmy Parrot endemic.
history
The island has probably been in existence since around 1500 BC. Inhabited by Melanesians . The area came under German administration in 1885 and belonged to German New Guinea since 1899 . During the First World War the island was conquered by Australian troops and after the war it was administered as a mandate of the League of Nations of Australia.
The island was occupied by Japan from 1942 to 1944, but returned to Australian administration in 1949 until Papua New Guinea became independent in 1975.
Web links
- Rambutyo, Oceandots.com (further information & pictures) ( Memento from December 23, 2010 in the Internet Archive ) (engl.)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Rambutjo . In: Heinrich Schnee (Ed.): Deutsches Koloniallexikon . Volume 3: P - Z. Quelle & Meyer, Leipzig 1920, p. 124.
- ↑ National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (Ed.): Sailing Directions. 2010. Pacific Islands (PDF file; 4.84 MB). National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, Springfield VA 2010.
- ^ Admiralty Islands. Scale 1: 500,000. Army Map Service, Washington DC 1942.
- ^ Languages of Papua New Guinea . In: M. Paul Lewis (Ed.): Ethnologue: Languages of the World. 16th edition. SIL International, Dallas TX 2009, online version.