Ribose phosphate diphosphokinase
| Ribose phosphate diphosphokinase | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Existing structural data: s. UniProt |
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 317 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer | |
| Cofactor | Mg 2+ | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | PRPS1 | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.7.6.1 , Diphosphotransferase | |
| Response type | Transfer of diphosphate | |
| Substrate | Ribose-5-phosphate + ATP | |
| Products | PRPP + AMP | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
The ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase (PRS-1) (formerly -Pyrophosphokinase) is the enzyme that in all living things, the synthesis of PRPP from ribose-5-phosphate catalyzed . This reaction is the basis for the biosynthesis of all nucleotides . Two isoforms of PRS-1 are still known in humans . Mutations in PRPS1 - gene can and to over-activity of the enzyme, this to increased hereditary risk of gout lead. Other PRPS1 mutations reduce the enzyme activity and are the cause of the so-called Rosenberg-Chutorian syndrome and a form of deafness ( ARTS syndrome ).
Catalyzed reaction
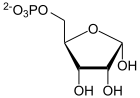
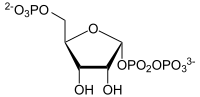
α- D- ribose-5-phosphate is converted to α- D -5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate.
Individual evidence
Web links
Wikibooks: Biochemistry and pathobiochemistry: alpha-D-5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate - learning and teaching materials
- d'Eustachio / reactome: 5-phosphoribose 1-diphosphate biosynthesis
- OrphaNet: Arts Syndrome
- OrphaNet: PRPP synthase superactivity