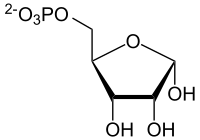
Ribose-5-phosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure of α- D- ribose-5-phosphate in the closed-chain form | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Ribose-5-phosphate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 5 H 11 O 8 P | |||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 230.11 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Ribose-5-phosphate is a natural pentose that is formed as an intermediate and product of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). As with many other metabolic carbohydrates, only the D form of the two enantiomers is important.
Production in the pentose phosphate route
Depending on the metabolic situation of the cell, it needs different metabolic products, which is reflected in the metabolic pathways. Ingested D - glucose is phosphorylated in the cell in order to prepare it for degradation; thus D - glucose-6-phosphate is formed . This is now mostly glycolytically degraded to pyruvate for the purpose of obtaining ATP , bacteria and archaea can metabolize glucose-6-phosphate in the Entner-Doudoroff path .
An alternative metabolic pathway is the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). The glucose-6-phosphate is oxidized and decarboxylated directly : In the oxidative part of the PPP, the double oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone and 6-phosphogluconate produces NADPH . 6-phosphogluconate is then added to ribulose-5-phosphate decarboxylated which is finally isomerized by the Phosphopentoseisomerase to ribose-5-phosphate. In the non-oxidative part, metabolic intermediates of the carbohydrate metabolism are formed through rearrangement reactions.
Importance in metabolism
Ribose-5-phosphate plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleotides , coenzymes and amino acids .
In nucleotide synthesis, 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) (and AMP) is initially formed from ribose-5-phosphate by reaction with ATP . In pyrimidine biosynthesis , the already synthesized pyrimidine ring is attached to the PRPP molecule, while the purine ring is synthesized on the PRPP.
In amino acid biosynthesis, the PRPP synthesized from ribose-5-phosphate z. B. needed for the carbon backbone of histidine . Ribose-5-phosphate is also a component of coenzymes , for example NADH and FAD .
Web links
- Entry for D-Ribose 5-phosphate in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) , accessed September 24, 2013.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Lehninger: Principles of Biochemistry , Freeman Edition.
- ^ Löffler, Petrides, Heinrich: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie , Springer-Verlag 2007.
- ^ Berg, Tymoczko, Stryer: Biochemie , Spectrum Academic Publishing House.