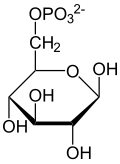
6-phosphogluconolactone
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||
| 6-phosphogluconolactone under physiological conditions | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | 6-phosphogluconolactone | |||||||||
| other names |
6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone |
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 11 O 9 P | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 256.10 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
6-phosphogluconolactone is a chemical compound that occurs as an intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway . In the first step of the pentose phosphate pathway, the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) catalyzes the oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate to 6-phosphogluconolactone. The enzyme's cofactor is NADP + , which is reduced to NADPH / H + :
Since this reaction is supposed to generate reduction equivalents in the form of NADPH , which are required in other metabolic synthesis pathways such as fatty acid biosynthesis , glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is specifically responsible for the conversion of NADP + to NADPH. NAD + can therefore not be used as a cofactor.
Catalyzed reaction
Glucose-6-phosphate is oxidized at the C1 atom by means of the cofactor NADP + . In the next step of the pentose phosphate pathway, 6-phosphogluconolactone is hydrolyzed to 6-phosphogluconate.
See also
literature
- Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt: Textbook of Biochemistry . Translation edited by Annette G. Beck-Sickinger and Ulrich Hahn. Wiley-VCH Verlag, 2002
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.