Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
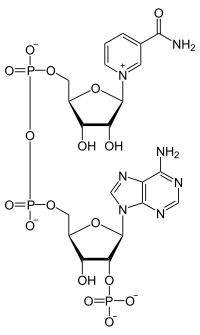
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 21 H 29 N 7 O 17 P 3 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless, hygroscopic, amorphous solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 744.41 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate , actually nicotinic acid amide adenine dinucleotide phosphate , abbreviated NADP , is a hydride ion transferring (H - = one proton / two electrons ) coenzyme that is involved in numerous redox reactions of the cell metabolism .
The IUPAC / IUBMB suggest the abbreviations NADP + for the oxidized form, NADPH for the reduced form and NADP in general.
The coenzyme was discovered by Otto Warburg in 1931 and was also known in the older specialist literature up to the early 1960s under the name triphosphopyridine nucleotide , abbreviated TPN , or under the names codehydrase II or codehydrogenase II or coenzyme II .
NADPH is a derivative of NADH , namely the phosphorylated form of the coenzyme NADH (on the ribose part, C2 '). There is a fundamental difference between NADH and NADPH in most biochemical reactions: NADH is obtained in catabolism from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle and is oxidized in the respiratory chain to produce ATP . In contrast, NADPH functions as a reducing agent in anabolism , it serves as a supplier of electrons and protons in reducing biosynthesis :
- During the synthesis of fatty acids , NADPH is oxidized to NADP + by the fatty acid synthase.
- When polyunsaturated fatty acids are broken down, NADPH is oxidized to NADP + (enzyme: 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase).
- in the so-called polyol route, d. H. When glucose is reduced to sorbitol , NADPH is oxidized to NADP + by a reductase .
- During the reduction of fatty acids to the corresponding fatty alcohol , NADPH is oxidized to NADP + by an acyl-CoA reductase .
- One source of NADPH is the direct oxidation of glucose-6-phosphate (G-6P) by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6P-DH) in the pentose phosphate pathway . The measurement of the amount of NADPH allows an exact determination of the amount of sugar converted in the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; the molar amount of NADPH is exactly proportional to the molar amount of sugar. In the further course of the 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase , another molecule of NADPH is produced.
- The NAD (P) H dependent glutamate dehydrogenase reduces NAD to NADH in the course of amino acid degradation.
- in green plants, NADPH is formed in the course of photosynthesis .
- In the citrate shuttle , NADPH is formed during the oxidative decarboxylation of oxaloacetate , which catalyzes an NADP-dependent malate enzyme .
The reducing power of NADPH can be transferred to glutathione .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Entry on nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on July 7, 2014.
- ↑ a b data sheet β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrate from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 16, 2011 ( PDF ).
