Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
| Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
Existing structural data: s. UniProt |
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 514/560 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer, homotetramer | |
| Cofactor | NADP | |
| Isoforms | Short, long | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | G6PD | |
| External IDs |
|
|
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 1.1.1.49 , oxidoreductase | |
| Response type | Dehydrogenation | |
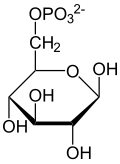
| Substrate | D-glucose-6-phosphate + NADP + | |
| Products | D-glucono-1,5-lactone-6-phosphate + NADPH + H + | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | GP6D | |
| Parent taxon | Chordates | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 2536 | 14381 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000160211 | ENSMUSG00000031400 |
| UniProt | P11413 | Q00612 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_000402 | NM_008062 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_000393 | NP_032088 |
| Gene locus | Chr X: 154.53 - 154.55 Mb | Chr X: 74.41 - 74.43 Mb |
| PubMed search | 2536 |
14381
|
The glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (alternative name: glucose-6-phosphate-1-dehydrogenase ; abbreviation: G6PD , G6PDH ) is in all chordates known enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate into 6-phosphogluconolactone accomplished . This chemical reaction is part of the pentose phosphate pathway in metabolism . Mutations in the G6PD gene can lead to defects in the encoded enzyme and thus to a G6PD deficiency .
G6PD is an enzyme from the group of oxidoreductases . It is a homodimeric or homotetrameric protein and occurs in two isoforms : a short isoform with a molar mass of 59 kDa and 514 amino acids , and a long isoform with 560 amino acids. The long isoform is found in lymphoblasts , granulocytes, and sperm cells . The short isoform is found in the liver and especially in the red blood cells ( erythrocytes ). Both isoforms bind NADP twice: once at the N-terminal end of the enzyme as a cofactor (between amino acids 27 and 210) and once as a structural element at the C-terminal end.
Catalyzed reaction
The task of the enzyme G6PD is to catalyze the reaction from glucose-6-phosphate to D-glucono-1,5-lactone-6-phosphate (6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone) with conversion of NADP + to NADPH .
Mutation of the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (G6PD) gene in section q28 of chromosome X (Xq28) in humans (DEHUG6 locus) leading to the disorder of the 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, glucose or favism named .
swell
Textbooks
- RK Ohls, RK Christensen: Chapter 20. Diseases of the blood. In: RE Behrman, RM Kliegman, HB Jenson: Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics . 17th edition. Saunders, Philadelphia 2003, ISBN 0-7216-9556-6 .
- M. Right, HA Pearson: Chapter 295. Hemolytic Anemias. In: JA McMillan, CD Deangelis, RD Feigin, JB Warshaw, FA Oski: Oski's Pediatrics: Principles and Practice. 3. Edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999, ISBN 0-7817-1618-7 .
Databases
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. In: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man . (English), as of July 21, 2006.
- Entrez protein from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), National Library of Medicine (NLM), USA record 120731 . As of September 19, 2006. Information in English .
- SwissProt database, University of Geneva, Switzerland. Data record P11413 . As of September 19, 2006. Information in English .
- Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD), Institute of Medical Genetics, Cardiff, UK data set G6PD . As of September 23, 2006. Information in English .
Web links
- Private homepage on the G6PD deficiency ( Memento from October 8, 2007 in the Internet Archive )