Rima (river)
| Rima | ||
|
Sokoto catchment area |
||
| Data | ||
| location |
|
|
| River system | Niger | |
| Drain over | Sokoto → Niger → Atlantic Ocean | |
| source | The confluence of the two rivers Bunsuru and Gagere . 6 ° 28 ′ 5 ″ N , 13 ° 12 ′ 30 ″ E |
|
| Source height | 321 m | |
| muzzle | in the Sokoto coordinates: 13 ° 6 ′ 44 ″ N , 5 ° 14 ′ 17 ″ E 13 ° 6 ′ 44 ″ N , 5 ° 14 ′ 17 ″ E |
|
| Mouth height | 247 m | |
| Height difference | 74 m | |
| Bottom slope | 0.34 ‰ | |
| length | over 220 km | |
| Catchment area | about 105,000 km² | |
| Discharge A Eo : 105,000 km² at the mouth |
MNQ MQ Mq MHQ |
0 l / s 294 m³ / s 2.8 l / (s km²) 1290 m³ / s |
| Right tributaries | Tarka , Goulbi N'Kaba , Goulbin Maradi , Maggia | |
| Reservoirs flowed through | Goronyo Reservoir | |
|
Satellite image of the Goronyo Reservoir |
||
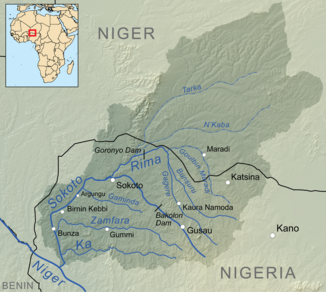
The Rima is a river in the extreme northwest of Nigeria .
course
It has its headwaters in the state of Katsina , like the main river Sokoto into which it flows and arises from the confluence of the rivers Bunsuru and Gagere . It initially flows in a north-westerly direction, towards the border with Niger. Shortly before the border, it changes its direction to the southwest. Its main tributaries are the Tarka and Goulbi N'Kaba , which practically split the estuary shortly after the Goronyo Reservoir , and Goulbin Maradi. Tarka and N'Kaba come from the desert climate of Niger and make up most of the Rima catchment area. Nevertheless, they hardly contribute any water and lie dry for the greater part of the year.
The Nigerian part of the Rima-Sokoto catchment area is 57,000 km² in size shortly after the confluence of the two rivers, with the Sokoto corresponding to 12,000 km². Virtually the entire part of the Niger catchment area belongs to the Rima.
Hydrometry
The flow rate of the river was measured in m³ / s at the mouth

ID
In some sources, the Rima is referred to as the main river and the Sokoto as the tributary.
use
The Rima is particularly relevant locally for irrigation in the arid climate.