Sorbitan monopalmitate
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
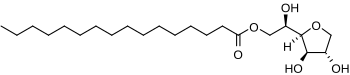
|
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Sorbitan monopalmitate | ||||||
| other names | |||||||
| Molecular formula | C 60 H 108 O 8 | ||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||
|
|||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Molar mass | 402.57 g mol −1 | ||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Sorbitan monopalmitate is a sorbitan fatty acid ester , an ester of sorbitol or 1,4-sorbitan anhydride ( sorbitan for short ). It is used in the food industry and in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations as an emulsifier . It is approved in the EU under the number E 495 as a food additive for certain foods (including various baked goods, ice cream, desserts and sugar products and creamer ). The permitted daily dose is 25 mg / kg body weight and day. It can also be used in medical gels that deliver active ingredients transdermally to the patient.
properties
Pharmaceutically used sorbitan monopalmitate is a mixture of partial esters of sorbitol and its mono- and dianhydrides with mainly palmitic acid (at least 92.0%). The proportion of stearic acid is a maximum of 6.0%. Pharmaceutical sorbitan monopalmitate is a yellow to yellowish powder, waxy flakes or solid mass. It is practically insoluble in water, soluble in fatty oils and sparingly soluble in ethanol 96%. The melting temperature is 44 to 51 ° C. The HLB value is 6.7.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on E 495: Sorbitan monopalmitate in the European database for food additives, accessed on June 28, 2020.
- ↑ Entry on SORBITAN PALMITATE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on April 12, 2020.
- ↑ a b Sorbitan monopalmitate data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 23, 2020 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Alicja Mortensen, Fernando Aguilar u. a .: Re ‐ evaluation of sorbitan monostearate (E491), sorbitan tristearate (E492), sorbitan monolaurate (E493), sorbitan monooleate (E494) and sorbitan monopalmitate (E495) when used as food additives. In: EFSA Journal. 15, 2017, doi: 10.2903 / j.efsa.2017.4788 .
- ↑ Jaleh Varshosaz, Abbas Pardakhty, Seied Mohsen Hossaini Baharanchi: Sorbitan monopalmitate-based proniosomes for transdermal delivery of chlorpheniramine maleate . In: Drug Delivery . tape 12 , no. 2 , 2005, ISSN 1071-7544 , p. 75-82 , doi : 10.1080 / 10717540490446044 , PMID 15824032 .
- ↑ Kamal K. Upadhyay, Chandraprabha Tiwari, Ajay J. Khopade, Himadri B. Bohidar, Sanjay K. Jain: Sorbitan ester organogels for transdermal delivery of sumatriptan . In: Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy . tape 33 , no. 6 , 2007, ISSN 0363-9045 , p. 617-625 , doi : 10.1080 / 03639040701199266 , PMID 17613026 .
- ↑ European Pharmacopoeia , 8th edition, basic work 2024, p. 4856.
- ↑ Sorbitan Esters (Sorbitan Fatty Acid Esters) . In: Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients , 6th edition. RC Rowe, PJ Sheskey, ME Quinn. Pharmaceutical Press, London, 2009. p. 675 ff.