Suboxides
Suboxides (from Latin sub = under) are chemical compounds of oxygen to more electropositive elements, in which fewer oxygen atoms are bound than would be expected based on the valency of oxygen. The formal oxidation state of the other element is therefore below +1 in these compounds. To compensate for this, there are element-element bonds in this connection class. Suboxides are mainly known from the alkali metals rubidium and cesium as well as from boron and carbon .
Suboxides are usually very unstable and disintegrate with the formation of the more stable oxides .
Alkali metal suboxides
The heavy rubidium and cesium are the only alkali metals that form suboxides. They are very reactive, colored solids that show electrical conductivity . The suboxides are made from the elemental alkali metals and small, precisely defined amounts of oxygen. This can be done, for example, by decomposing suitable oxides such as silver or mercury oxide.
All alkali metal suboxides react very easily with water , oxygen or carbon dioxide to form the more stable oxides or hyperoxides .
Rubidium suboxides
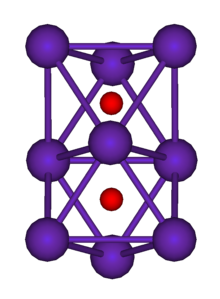
The most important rubidium suboxide has the ratio formula Rb 9 O 2 . It is a copper-colored solid with a melting point of 40.2 ° C. The structure consists of individual Rb 9 O 2 clusters. In these the nine Rb atoms are arranged in two face-sharing octahedra . The oxygen atoms are each in the middle of the octahedron.
Further rubidium can also be stored around the individual clusters , for example with bronze-colored Rb 6 O there are three rubidium atoms per cluster. However, these are more unstable, so Rb 6 O decomposes at −7.7 ° C
Cesium suboxides
Cesium also forms a number of suboxides. The most important cesium suboxide has the formula Cs 11 O 3 . It is a purple solid with a melting point of 52.5 ° C. As with rubidium, the structure consists of face-sharing octahedra with the oxygen atoms in the middle. However, there are three octahedra in cesium instead of two as in rubidium.
As with rubidium, additional metal atoms can also be incorporated in cesium. Compounds with up to 10 additional cesium atoms are known, which corresponds to a ratio formula of Cs 7 O.
Cesium suboxides arise in certain photocathodes , the so-called S1 photocathodes, which consist of thin silver , cesium and cesium oxide layers. The suboxides formed by the reaction of cesium with cesium oxide are responsible for ensuring that the cathode can also adsorb light in the infrared range and emit electrons accordingly .
Carbon suboxides
Carbon suboxide C 3 O 2 differs significantly from the alkali metal suboxides. It is a molecularly structured, gaseous compound that easily polymerizes to a brown-red solid. Also Pentakohlenstoffdioxid C 5 O 2 is known.
Boron suboxides
Several boron suboxides are known. The trigonal suboxide B 6 O is one of the hardest known materials with a hardness comparable to that of cubic boron nitride . Another boron suboxide is boron (I) oxide (B 2 O) x , which is isoelectronic to graphite and has a corresponding structure.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c A. F. Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1286.
- ↑ Arndt Simon: Chemistry and physics of solids - different perspectives, same concerns . In: Chemistry in our time , 1988, 22, 1, pp. 1-8, doi : 10.1002 / ciuz.19880220102 .
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 901.
- ↑ Duanwei He et al .: Boron suboxide: As hard as cubic boron nitride . In: Applied Physics Letters, 2002, 81, pp. 643-645, doi : 10.1063 / 1.1494860 .
- ^ AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 , p. 1105.
literature
- AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 102nd edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 2007, ISBN 978-3-11-017770-1 .
- Arndt Simon : Group 1 and 2 suboxides and subnitrides - metals with atomic size holes and tunnels . In: Coordination Chemistry Reviews , 1997, 163, pp. 253-270, doi : 10.1016 / S0010-8545 (97) 00013-1 .