Suosan
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
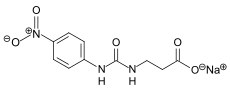
| Suosan sodium salt | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Suosan | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 10 H 10 N 3 O 5 Na | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 275.20 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||
| Melting point |
240 ° C (decomposition) |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water (62 g l −1 at 20 ° C, sodium salt) |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Suosan is an artificially produced sweetener . From a chemical point of view, it is the sodium salt of β-4-nitroanilidasepartamic acid, a urea derivative .
Suosan is around 700 times sweeter than sucrose . In acidic solutions, Suosan is said to taste better than saccharin. Due to its yellowish color, Suosan, like Douxan , is a dye-like sweetener.
history
Suosan was discovered in 1948 by S. Petersen and E. Müller. Since then it has been extensively investigated, but has practically never been used, since the toxic 4-nitroaniline is released when it decomposes .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Switzerland. Food book: Sweeteners ( Memento from January 15, 2005 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Hans-Dieter Belitz , Werner Grosch and Peter Schieberle: Textbook of food chemistry . 6., completely revised Edition 2008, Springer-Verlag Berlin; ISBN 3-540-73201-2 ; doi : 10.1007 / 978-3-540-73202-0 ; P. 451.
- ^ C. Nofre, JM Tinti & FO Chatzopoulos: Glycine and β alanine derivatives as sweetening agents . U.S. Patent 4,877,895.