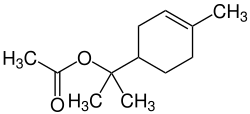
Terpinylacetate
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| Simplified structural formula without stereochemistry | |||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Terpinylacetate | ||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 20 O 2 | ||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless liquid with a characteristic odor |
||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 196.29 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||
| density |
0.953 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
||||||||||||
| boiling point |
220 ° C |
||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.465 (20 ° C) |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | |||||||||||||
Terpinylacetate is a chemical compound from the group of esters of terpineol .
Occurrence
Terpinylacetate occurs mainly in the α-, but also in the δ-form naturally in essential oils of cypress, cardamom, laurel, pine and others.
Extraction and presentation
Terpinylacetate can be obtained by acetylating terpineol or mixed isomeric terpineols using acetic anhydride and anhydrous sodium acetate . It can also be made from 1,8-cineole . The compound was first synthesized in 1888.
properties
Terpinylacetate is a colorless liquid with a characteristic odor that is soluble in essential oils and most organic solvents .
use
Terpinylacetate is used as a fragrance ( lavender and bergamot type) and as an intermediate in the manufacture of carvone .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f George A. Burdock: Encyclopedia of Food and Color Additives . CRC Press, 1997, ISBN 978-0-8493-9414-0 , pp. 2995 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c d e f g data sheet α-Terpinyl acetate, FG from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on November 8, 2018 ( PDF ).
- ↑ David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics A Ready-reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data . CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-0595-5 , pp. 510 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ Klaus Roth: Chemical delicacies . John Wiley & Sons, 2014, ISBN 978-3-527-33739-2 , pp. 199 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Norbert A. Braun, Manfred Meier u. a .: δ-Terpinyl Acetate. A New Natural Component from the Essential Leaf Oil of L. (Lauraceae). In: Journal of Essential Oil Research. 13, 2001, p. 95, doi : 10.1080 / 10412905.2001.9699624 .
- ↑ Ean-Tun Liaw, Kuan-Ju Liu: Synthesis of terpinyl acetate by lipase-catalyzed esterification in supercritical carbon dioxide. In: Bioresource Technology. 101, 2010, p. 3320, doi : 10.1016 / j.biortech.2009.11.081 .
- ↑ Kurt Bauer, Dorothea Garbe, Horst Surburg: Common Fragrance and Flavor Materials Preparation, Properties and Uses . John Wiley & Sons, 2008, ISBN 3-527-61237-8 , pp. 69 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
