Tetramethylazodicarboxamide
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
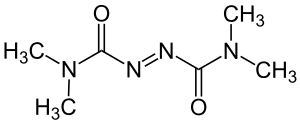
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Tetramethylazodicarboxamide | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 12 N 4 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
yellow powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 172.19 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
112 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Tetramethylazodicarboxamide is a chemical compound used in biochemistry to oxidize thiols to disulfide bridges in proteins. It was also used instead of diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD) in the Mitsunobu reaction .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Tetsuto Tsunoda, Hiroto Kaku: N, N, N′N′-Tetramethylazodicarboxamide . In: Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis . John Wiley & Sons, 2003, doi: 10.1002 / 047084289X.rn00274 .
- ↑ a b Entry on 1,1′-Azobis (N, N-dimethylformamide) at TCI Europe, accessed on April 15, 2013.
- ↑ a b data sheet 1,1′-Azobis (N, N-dimethylformamide) from fluorochem, accessed on May 11, 2018.
- ↑ Current Medicinal Chemistry . August 1996, p. 296 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
