Transimpedance amplifier
A transimpedance amplifier (also known as a current-voltage converter or IU converter ) is an electrical amplifier that converts an input current into a proportional output voltage. It is therefore a current-controlled voltage source .
The ratio of output voltage to input current is called transimpedance
which has the same unit as an impedance (ohm).
Ideally, a transimpedance amplifier has zero input resistance and a very low output resistance.
Function description
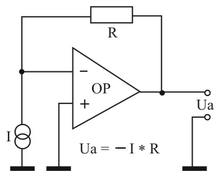
A typical circuit of a transimpedance amplifier is shown opposite. The amplifier circuit consists of a “conventional”, voltage-controlled operational amplifier (VV-OPV) and should not be confused with the component of the current-fed back operational amplifier (CV-OPV).
The non-inverting input of the operational amplifier is grounded; A current signal is sent to the inverting input. The operational amplifier is fed back with an ohmic resistor . The operational amplifier , makes its very high gain and the negative feedback by that the voltage difference between the two inputs OPV is only a fraction of a millivolt. This is the point of connection of power supply , and the OPV input a so-called virtual ground that is actually one of streams such as short-circuit after mass acts. The current to be measured causes a constant zero voltage drop.
As a result of the knot rule , according to which the sum of all currents with the correct sign at this point is zero (ideally no current flows into the OPV input), the output voltage is:
or the gain or transimpedance in volts per ampere (= ohms):
In practice, the sign means that a measuring current flowing away from ground (i.e. flowing towards the OPV) causes a negative output voltage. The advantage over current measurement using a shunt is the negligible voltage drop of the current measurement using a transimpedance amplifier.
application
The transimpedance amplifier is used, among other things, in measurement technology to enable precise measurements of small currents (e.g. photo currents ). A few nanoampere input current or nanowatt light output can be precisely measured. However, the higher the sensitivity, the lower the cutoff frequency.
An operating mode that is suitable for measurement purposes for the photodiodes typically operated on it is the quasi-short circuit: the photodiode generates a photocurrent without a voltage being applied to its connections. In this mode there is no residual current from the photodiode, which interferes with reverse operation. Photodiodes operated in a quasi-short circuit are usually connected with their cathode to the input and the anode to ground, so that a positive output voltage results when light falls and the OPV often does not need a negative operating voltage.
Since the alternating voltage on the photodiode is 0 in the ideal transimpedance amplifier, its junction capacitance only plays a role for the behavior of the amplifier - it causes a phase shift and frequency limitation of the feedback signal. Significantly higher cut-off frequencies are achieved when the diode is reverse-biased, as this reduces the junction capacitance. 5 MHz bandwidth with a photodiode junction capacitance of 50 pF and a transimpedance of 200 V / mA can be achieved (OPA657).
In order to be able to measure over several orders of magnitude, there are switchable or programmable transimpedance amplifiers. There are also logarithmizing transimpedance amplifiers that can be used to measure over many orders of magnitude without switching.
swell
- ↑ Optoelectronics II , G.Winstel C.Weyrich, Springer Verlag 1986. P. 86, ISBN 3-540-16019-1
- ↑ Optical information transmission with fiber optics , D.Rosenberger, expert verlag 1982, p. 117, ISBN 3-88508-809-6
- ↑ http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/opa657.pdf
literature
- Ulrich Tietze, Christoph Schenk: Semiconductor circuit technology . 12th edition. Springer, Berlin 2002, ISBN 3-540-42849-6 .