UV radiation protection
UV radiation protection includes measures to protect against the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation (UV). In numerous countries there are legal regulations, guidelines and standards for the implementation of protection.
Basics
| UV-A blockers |
|---|
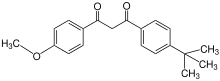 Avobenzone |
 Ecamsul |
 Methyl antranilate |
| UV-B blockers |
 Homo salad |
 Octyl methoxycinnemate |
| UV-A / B blockers |
 Oxybenzone |
 Sulisobenzone |
Areas of UV radiation
The ultraviolet radiation (UV) gets into the areas
- UV-A ( wavelength 315-400 nm ),
- UV-B (280-315 nm) and
- UV-C (100-280 nm)
divided. It belongs to the field of non-ionizing radiation . UV radiation promotes the formation of vitamin D , but also sunburn and skin cancer . Depending on the different mechanisms of action of UV-A, UV-B and UV-C, different limit values apply.
UV sources
UV sources can be roughly divided into
- natural sources ( sun )
- artificial sources (UV lamps or radiators, z. B. Gas discharge lamps such as Quecksilbermittel- or -hochdruckstrahler, doped mercury lamps, quartz-halogen lamp, deuterium lamp, and various gas lasers and light emitting diodes , arc of welding machines )
Artificial UV sources with low radiation intensity are used, among other things, in solariums, in the food industry or in banknote validators.
Furthermore, UV emitter systems with high radiation intensity are used in industrial applications. Examples of this are the printing industry (hardening of printing inks on paper, foils, plastic and glass bodies, etc.), electronics industry (hardening of protective lacquers and lettering), general industry (hardening of lacquers and colors, lettering, adhesive applications, etc.), water treatment (disinfection effect ) as well as applications in many other industrial sectors.
Biological effect
The UV radiation has a thermal effect on the skin and eyes (especially UV-A to infrared radiation ) and photochemical (UV-A - UV-C). UV radiation with a wavelength below 190 nm has no effect as it is completely absorbed by the air. UV radiation of different frequencies / wavelengths penetrates the tissue to different depths. Therefore the type of damage is also dependent on the wavelength.
The dose is decisive for tissue damage. It is the product of the irradiance and the exposure time.
Effect on the skin
The skin is made up of
- Upper skin ( epidermis )
- Dermis ( dermis or corium)
- Under the skin ( subcutaneous )
UV-C is completely absorbed on the surface of the skin. UV-B and UV-A mainly penetrate the dermis. The visible light is partially absorbed in all 3 skin layers.
The following harmful effects can occur:
- Sunburn (erythema)
- Pigmentation (tan)
- Skin cancer (carcinogenesis)
- Skin aging
Effect on the eye
When UV radiation interacts with the eye , the cornea , lens and retina are of particular importance . UV-C is completely absorbed by the cornea. UV-B is absorbed partly on the cornea and partly in the lens. UV-A is also partly absorbed by the cornea and partly by the lens, about 1–2% penetrate to the retina.
The following harmful effects can occur:
- Corneal inflammation ( keratitis )
- Cataract ( cataract )
- Inflammation of the retina ( retinitis )
- Retinal melanoma
Directives and limit values
The most important internationally valid limit values are issued by
- American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists
- "Threshold limit values for chemical substances and physical agents; Biological Exposure Indices", Cincinnati, 1997
- International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection of the International Radiation Protection Association
- "Guidelines on limits of exposure to ultraviolet radiation of wavelengths between 180 nm and 400 nm", Health Physics 49: 331-340, 1985
- "Proposed change to the IRPA 1985 guidelines on limits of exposure to ultraviolet radiation", Health Physics 56: 971-972, 1989
- Commission International de l´Eclairage - International Commission on Illumination
- "Erythemal reference function function and standardized erythema dose", CIE S007 / E-1998
Due to the different strengths of the effect depending on the wavelength, the electromagnetic spectrum of the radiation must be weighted with biological factors. The following evaluation curves are used:
| tissue | rating | Directive |
|---|---|---|
| lens | UV-A | ACGIH, ICNIRP |
| Cornea | s λ | ACGIH, ICNIRP |
| skin | s λ , erythemal | ACGIH, ICNIRP & CIE |
The evaluation according to the three different guidelines can result in simultaneous exceeding of one limit value and falling below the other.
Protective measures
To protect the skin from harmful UV radiation, normal clothing, special UV protective clothing ( sun protection factor 40–50) and sun cream with a high sun protection factor can be used. Sunglasses with UV protection or special protective goggles are used to protect the eyes .
See also
Web links
- Susanne Eichacker: "UV protection through textiles?" (PDF; 273 kB) Flight information service of the Helmholtz Zentrum München , accessed on August 23, 2008 .