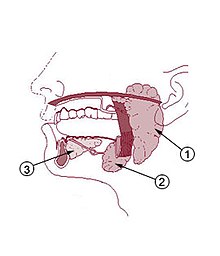
Submandibular gland
The paired applied submandibular gland or latin submandibular gland (in veterinary anatomy as mandibular gland hereinafter) is one of three major salivary glands . It is a mixed seromucous gland and produces with the other glands together the saliva ( Saliva ). The lower salivary gland supplies most of the total amount of saliva. It lies on both sides at the lower jaw angle, between the lower jaw and the digastric muscle in the so-called submandibular trigonum , and here within the superficial sheet of the cervical fascia ( fascia cervicalis ). The posterior part of the gland, like a hook, encompasses the posterior border of the mylohyoid muscle . The palpable salivary gland can be mistaken for less experienced people with a swelling of the mandibular lymph nodes directly to the side of it .
The duct of the gland ( ductus submandibularis , Wharton's duct ) opens together with that of the large sublingual gland on the caruncula sublingualis ("starvation wart"), a small papilla on the side of the tongue frenulum .
Innervation and blood supply
The innervation of the mandibular salivary gland is carried out by the vegetative nervous system . The parasympathetic nerve fibers originate from the upper salivary gland nucleus ( nucleus salivatorius superior ) and leave the cranial cavity with the chorda tympani , a branch of the seventh cranial nerve ( nervus facialis ). These fibers connect to the lingual nerve and thus reach the submandibular ganglion (referred to as the mandibular ganglion in animals ), where they are switched and then move to the mandibular and sublingual salivary glands.
The blood supply takes place through the facial artery , the venous outflow through the submental vein and the sublingual vein. Regional lymph nodes are the chin ( Nodi lymphoidei submentales ) and the lower jaw ( Lymphonodi submandibulares ).
Microscopic anatomy
The submandibular gland is a mixed seromucosal gland. In the microscopic sectional image one sees serous, ie thin liquid secretion producing end pieces, which occasionally open into mucous, ie thick liquid secretion tubules. Switching pieces, tubes made of flat epithelium , form the transition to the excretory duct system.
literature
- Karl Zilles, Bernhard Tillmann : Anatomy . Springer, 2010, ISBN 978-3-540-69483-0 , pp. 438 .
- Franz-Viktor Salomon: oral cavity, cavum oris . In: Franz-Viktor Salomon et al. (Hrsg.): Anatomie für die Tiermedizin . 2nd Edition. Enke, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8304-1075-1 , pp. 239-264 .