White point
The white point defines the achromatic color “white” (with full luminance ) in color spaces , color tables and in the technical devices that are used to input or output colors . The exact position of the white point depends on the type of lighting.
Definitions
The term “white point” is used with different meanings; the benefit is to avoid the inadvertent color cast . In order to achieve a fixed dimension in white , a minimum luminance is usually prescribed for calibration or profiling .
1. For the calibration of devices, the white point is the controlled variable that
- in color monitors for the full radiation power with the same intensity of color systems is
- stands for the brightest achromatic point when tuning a digital camera ( white balance ).
- The calibration then takes place between the white point = 100% and the black point = 0%.
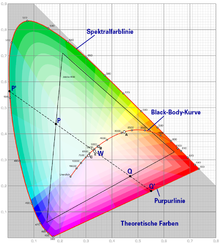
2. In the standard color table, the defined white point is the equivalence point x = y = z = 0.3333 ("W" in the figure). However, this same energy position of the white point only applies to the illumination e .
In general there are several white points, the location of which depends on the type of lighting. In the XYZ system , they lie on the black body curve of the associated color body (also achromatic line or in the figure "black body curve"); this curve results from the color temperatures of the Planck radiators , which correspond to the lighting used.
According to the standardized measurement conditions, the white point is always displayed on the plane for the value Y = 100; This value should be named more precisely than the brightness reference value A , which is the same size as Y.
The influence of the type of lighting on the color tone is balanced out by adjusting the position of the white point to the type of lighting.
Location of some white points
The white point is the location of neutral white on the two-dimensional color type surface ( chromaticity space).
- 2 ° normal observer of the CIE system in 1931
- 10 ° field of view according to CIE 1964
- Light type P (as above): x P = 0.5407, y P = 0.4104.
- for D65 (with x + y + z = 1) on the triple {x, y, z} = {0.3138; 0.3310; 0.3552}.
- Equivalent illuminant E: x = y = z = 0.3333
- The same considerations apply to other color spaces . In the u'-v 'diagram for D50: u' = 0.2092, v '= 0.4881.
Related terms
Achromatic point
In a two-dimensional representation, the location of neutral white apparently coincides with the location of neutral black or neutral gray . For this reason, the term achromatic point is also found. However, since Y = 100 is assumed as the third coordinate for the display, the designation white point is correct.
Achromatic axis
In the three-dimensional color spaces (Rösch color bodies ), the white point corresponds to a neutral gray axis, also called achromatic axis, because at this point - regardless of the constitution - all achromatic colors between white and black are displayed. The white point represents one end of the achromatic axis which, in the two-dimensional representation, is perpendicular to the surface or parallel to the viewing direction; the other end of the achromatic axis is the black point with Y = 0.
See also
Web links
- Calculation of the white point from the color temperature of the black body
- Links to color management and calibration
- Color-Security.de
Individual proof
- ↑ Manfred Richter: Introduction to colorimetry