Chromaticity

In colorimetry, color type (identical colors) denotes the combination of colors according to hue and color saturation , but with different brightness .
Depending on the application level or perception category, the type of color is based on different primary or original colors :
- on the three color stimuli of the three-color theory (red, green, blue), or
- on the four opposing basic colors of the opposite color theory (red-green and yellow-blue).
The achromatic colors are only evaluated indirectly.
Basics
The term chromaticity is defined in CIE 845-03-34 and, based on this, also in DIN 5033 .
According to Graßmann's laws, a color can be clearly identified by three parameters. A color stimulus is analyzed by the three types of cones in the eye. As a result, three color valences are "filtered out" from the continuous spectrum .
The physical cause of color perception is the multitude of values, in each case intensities over the wavelengths λ:
- the degree of remission β (λ) for remission of body colors
- the transmittance τ (λ) for transmission to filters
- the reflectance σ (λ) for reflection in light colors .
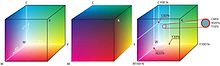
The sense of sight turns this into a triple number of sensations, which - processed in the nervous system - result in the color impression . These three parameters can be represented in different ways in a three-dimensional color space .
The color space can be selected so that the brightness is assigned to its own axis. The remaining coordinates then give the color type. The brightness can also be viewed as a brightness reference value A or a neutral gray value .
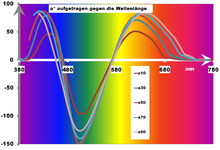
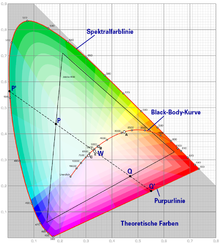
In the CIEXYZ color system, this results in the xy color area (chromaticity diagram). In the L * a * b * color space of the CIE system from 1976, the color type is specified in the a * -b * plane, with the a * axis for the green-red and the b * axis for the blue -Yellow values stands. This form of color representation offers the advantage that it enables information corresponding to the familiar color wheel . These chromaticity coordinates in the Cartesian system can be converted into polar coordinates C – h ° ( chroma , hue ), which meet the inexperienced and therefore more practicable understanding of color and correspond to the color wheel.
In the RGB color space and in the CMYK color space , the representation of the color type does not make sense, since the emission colors of the three phosphors , the three color filters or in the CMYK space the three color pigments were used as a basis; the fourth color pigment K (black) is, by definition, only an addition to achieve “depth”. In both color spaces, brightness is not a direct parameter and the color type is therefore placed over the entire room.
Color trio
A rule of mixing three basic colors has been common among painters since the late Middle Ages . The use of three color sources is largely sufficient for technical devices and processes . In the case of color picture tubes , these are the three RGB phosphors red, green and blue. Like the CMY colors, they form a color trio . The color trio goes back to studies by the Englishman James Sowerby , who published his work A New Elucidation of Colors, dedicated to Isaac Newton , in 1809 . On the one hand, Sowerby wanted to emphasize the importance of lightness and darkness, and on the other hand to point out once again that colored light and colored matter differ in their behavior.
In his investigations, Sowerby assumed the three basic colors red , yellow and blue .
In further investigating the relationships between color perception, Hering added green with his four-color theory . The Englishman Thomas Young found in his investigations and the resulting theory, the Theory of Trichromatic Vision , that the eye already combines all other color valences by perceiving three color quality tones. But Young used red, green and blue as the basis, so he replaced Sowerby's yellow with green.
Young's theory was experimentally deepened in the 20th century. The pigments on the cones on the retina are particularly good at perceiving red, green or blue light. On the other hand, the psychological processes of color perception, especially the role of visual brightness and the type of color, led to the clarification of the connection with the theory of opposing colors.
literature
- J. Sowerby: A New Elucidation of Colors, Original, Prismatic, and Material: Showing their Concordance in Three Primitives, Yellow, Red, and Blue: and the Means of Producing, Measuring, and Mixing Them: with Some Observations on the Accuracy of Sir Isaac Newton. London 1809.
- S. Wurmfield: Color Documents: A Presentational Theory . Organized by Hunter College Art Gallery, New York 1985.
- John Gage: Cultural History of Color: From Antiquity to the Present . Maier, Ravensburg 1994, p. 221.