Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum - EM spectrum for short and more precisely called the electromagnetic wave spectrum - is the entirety of all electromagnetic waves of different wavelengths . The light spectrum , also color spectrum , is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to humans.
The spectrum is divided into different areas. This classification is arbitrary and, for historical reasons, is based on the wavelength in the low-energy range. Wavelength ranges over several orders of magnitude with similar properties are grouped into categories such as light , radio waves , etc. A subdivision can also be made according to the frequency or the energy of the individual photon (see below). In the case of very short wavelengths, correspondingly high quantum energy, a classification according to energy is common.
Arranged according to decreasing frequency and thus increasing wavelength, the short-wave and therefore high-energy gamma rays are located at the beginning of the spectrum , the wavelength of which extends into atomic orders of magnitude. At the end there are the longest waves , the wavelengths of which are many kilometers.
The wavelength is converted into a frequency using the formula . Where is the speed of light .
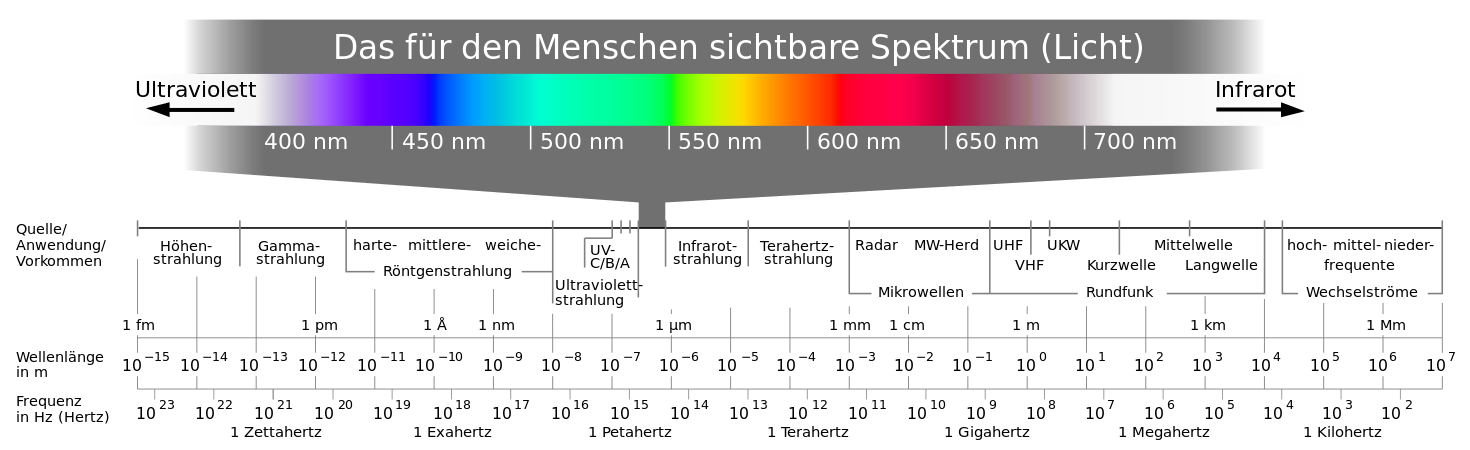
- Overview of the electromagnetic spectrum
The areas of the electromagnetic spectrum
| Designation of the frequency range |
Sub-designation | wavelength | frequency |
Photons - energy |
Generation / excitation | Technical commitment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| from | to | from | to | |||||
| Low frequency | Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) | 10 mm | 100 mm | 3 Hz | 30 Hz | > 2.0 · 10 −33 J > 12 feV |
Floor dipole , antenna systems | Traction current |
| Super Low Frequency (SLF) | 1 mm | 10 mm | 30 Hz | 300 Hz | > 2.0 · 10 −32 J > 120 feV |
Mains frequency , (formerly) submarine communication | ||
| Ultra Low Frequency (ULF) | 100 km | 1000 km | 300 Hz 0.3 kHz |
3000 Hz 3 kHz |
> 2.0 · 10 −31 J > 1.2 peV |
|||
| Very Low Frequency (VLF) Myriameter waves Longitudinal waves (SLW) |
10 km | 100 km | 3 kHz | 30 kHz | > 2.0 · 10 −30 J > 12 peV |
Submarine communication ( DHO38 , ZEVS , Sanguine , SAQ ), radio navigation , heart rate monitors | ||
| Radio waves | Long wave (LW) | 1 km | 10 km | 30 kHz | 300 kHz | > 2.0 · 10 −29 J > 120 peV |
Oscillator circuit + antenna | Long wave radio , DCF77 , induction hob |
| Medium wave (MW) | 100 m | 1000 m | 300 kHz | 3 MHz | > 2 · 10 −28 J > 1.2 neV |
Medium wave broadcasting , HF surgery , (1.7 MHz-3 MHz boundary wave , short wave broadcasting ) | ||
| Short wave (KW) | 10 m | 100 m | 3 MHz | 30 MHz | > 1.1 · 10 −27 J > 12 neV |
Boundary wave , shortwave broadcasting , HAARP , diathermy , RC model making | ||
| Ultra short wave (VHF) | 1 m | 10 m | 30 MHz | 300 MHz | > 2.0 · 10 −26 J > 120 neV |
Oscillator circuit + antenna | Radio , television , radar , magnetic resonance imaging | |
| Microwaves | Decimeter waves | 10 centimeters | 1 m | 300 MHz | 3 GHz | > 2.0 · 10 −25 J > 1.2 µeV |
Magnetron , klystron , burl , cosmic background radiation
Excitation of nuclear magnetic resonance and electron spin resonance , molecular rotations |
Radar , magnetic resonance imaging , cellular communications , television , microwave oven , WiFi , Bluetooth , GPS , 5G |
| Centimeter waves | 1 cm | 10 centimeters | 3 GHz | 30 GHz | > 2.0 · 10 −24 J > 12 µeV |
Radar , radio astronomy , directional radio , satellite broadcasting , WLAN , 5G | ||
| Millimeter waves | 1 mm | 1 cm | 30 GHz | 300 GHz 0.3 THz |
> 2.0 · 10 −23 J > 120 µeV |
Radar , radio astronomy , directional radio | ||
| Terahertz radiation | 30 µm | 3 mm | 0.1 THz | 10 THz | > 6.6 · 10 −23 J > 0.4 meV |
Synchrotron , free-electron laser | Radio astronomy , spectroscopy , imaging techniques | |
| Infrared radiation (heat radiation) | Far infrared | 50 µm | 1 mm | 300 GHz | 6 THz | > 2.0 · 10 −22 J > 1.2 meV |
Heat radiator , synchrotron
Molecular vibrations |
Infrared spectroscopy , Raman spectroscopy , infrared astronomy |
| Mid infrared | 3.0 µm | 50 µm | 6 THz | 100 THz | > 4.0 · 10 −21 J > 25 meV |
Carbon dioxide laser , quantum cascade laser | Thermography | |
| Near infrared | 780 nm | 3.0 µm | 100 THz | 385 THz | > 8.0 10 −20 J > 500 meV |
Nd: YAG laser , laser diode , light emitting diode | Remote control , data communication ( IRDA ), CD | |
| light | red | 640 nm | 780 nm | 384 THz | 468 THz | 1.59-1.93 eV |
Radiant heaters ( incandescent lamp ), gas discharge ( neon tube ), dye and other lasers , synchrotron , light-emitting diode
Excitation of valence electrons |
DVD , laser pointer , data transmission ( optical fiber ) Red, green: laser level , lighting , colorimetry , photometry , red, yellow, green: traffic light system , purple: Blu-ray disc |
| orange | 600 nm | 640 nm | 468 THz | 500 THz | 1.93-2.06 eV | |||
| yellow | 570 nm | 600 nm | 500 THz | 526 THz | 2.06-2.17 eV | |||
| green | 490 nm | 570 nm | 526 THz | 612 THz | 2.17-2.53 eV | |||
| blue | 430 nm | 490 nm | 612 THz | 697 THz | 2.53-2.88 eV | |||
| violet | 380 nm | 430 nm | 697 THz | 789 THz | 2.88-3.26 eV | |||
| UV rays | Near UV (" black light ") | 315 nm | 380 nm | 789 THz | 952 THz | 3.26-3.94 eV | Gas discharge , synchrotron , excimer laser , light emitting diode | Black light fluorescence , phosphorescence , bank note checking , photolithography , disinfection , UV light , spectroscopy |
| Medium UV (" Dorno radiation") | 280 nm | 315 nm | 952 THz | 1071 THz 1 PHz |
3.94-4.43 eV | |||
| Far UV | 200 nm | 280 nm | 1 PHz | 1.5 PHz | 4.43-6.2 eV | |||
| Vacuum UV | 100 nm | 200 nm | 1.5 PHz | 3 PHz | > 9.9 · 10 -19 J 6.2-12 eV |
XUV tube , synchrotron , nanoplasm | EUV lithography , X-ray microscopy , nanoscopy | |
| EUV | 10 nm | 121 nm | 2.5 PHz | 30 PHz | > 5.0 · 10 −18 years 10.2-120 eV |
|||
| X-rays | 10 pm | 10 nm | 30 PHz | 30 EHz | > 2.0 · 10 −16 J > 120 eV |
X-ray tube , synchrotron
Excitation of internal electrons , Auger electrons |
medical diagnostics , security technology, X-ray structure analysis , X-ray diffraction , photoelectron spectroscopy , X-ray absorption spectroscopy | |
| gamma rays | 10 pm | 30 EHz | > 2.0 · 10 −14 J > 120 keV |
Radioactivity , annihilation
Excitation of core states |
medical radiation therapy , Mössbauer spectroscopy | |||
See also
literature
- DIN 5031 Part 7: Radiation physics in the optical field and lighting technology; Designation of the wavelength ranges. January 1984 (IR, VIS and UV).
Web links
- Poster "Electromagnetic Radiation Spectrum" (PDF, English; 992 kB)
- The electromagnetic spectrum in the world of physics
Individual evidence
- ↑ are as defined in the Radio Regulations, 2012 edition, Article 1.5 also to the radio waves.
- ↑ German Institute for Standardization (Ed.): Radiation physics in the optical field and lighting technology; Designation of the wavelength ranges. DIN 5031 part 7, January 1984.