Xenonic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Xenonic acid | ||||||||||||
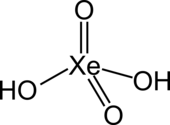
| Molecular formula | H 2 XeO 4 | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 197.31 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
||||||||||||
| pK s value |
10.5 |
||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Xenonic acid is an acid of the noble gas xenon . Their salts are the Xenate XeO 4 2− and the Hydrogenxenate HXeO 4 - . Their existence was predicted by Linus Pauling .
Extraction and presentation
Xenonic acid can be produced by hydrolysis of xenon (VI) oxide XeO 3 , whereby only a small part reacts to form the acid.
properties
Xenonic acid is a powerful oxidizing agent . In acidic solution it is able to oxidize iodine quickly. The acidic solution is only slightly acidic.
The hydrogen xenate ion HXeO 4 - can be produced by adding a base to xenon (VI) oxide .
The disproportionation of the hydrogen xenate ion gives rise to the perxenate ion XeO 6 4− .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c d A. F. Holleman, Egon Wiberg, Nils Wiberg: Inorganic Chemistry . Ed .: Nils Wiberg. Academic Press, 2001, ISBN 0-12-352651-5 , pp. 399 .
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Linus Pauling: The Formulas of Antimonic Acid and the Antimonates . J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1933, pp. 1895–1900 , doi : 10.1021 / ja01332a016 .
- ^ Howard H. Claassen: The Noble Gases . Heath, 1966, p. 65 .
- ↑ David W. Oxtoby, Wade A. Freeman, Toby F. Block: Chemistry 4th Edition . ISBN 0-03-033188-9 , chap. 4 , p. 87AP .




