Sorbitan
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||||||||||||||
| Structure without stereochemistry | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Sorbitan | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 6 H 12 O 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Solid, mostly as a dark colored oil or syrup |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 164.16 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
solid or liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
111-112 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water, methanol, ethanol, isopropanol |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
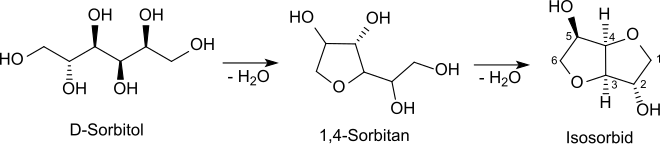
Sorbitan (short for sorbitol anhydride , also anhydrosorbitol ) is a mixture of several isomeric chemical compounds from the group of heterocycles and polyols . The mixture is formed during the elimination of one molecule of water from sorbitol (in the English literature sorbitol called) and consists mainly of 1,4- D -Sorbitanhydrid - a five-membered cyclic (, furanoid ') ether - in addition to the isomeric 2,5-furanoid anhydrosorbitol and the isomeric pyranoid 1,5-anhydrosorbitol. The splitting off of another molecule of water leads to isosorbide (1,4: 3,6-dianhydro- D- sorbitol).
Extraction and presentation
Sorbitan is produced by monomolecular dehydration from D- sorbitol together with other isomeric anhydro sugars from the sorbitol, mannitol and iditol series. The elimination of water takes place from approx. 120 ° C under acid catalysis by mineral acids, acidic ion exchangers or carrier-supported heteropoly acids at normal pressure, under vacuum or in supercritical water. The 1,4-anhydride is preferably formed under mild reaction conditions. Under more severe reaction conditions, dimolecular dehydration leads to the formation of isosorbide or intermolecular elimination of water to the formation of oligomers and polymers.
Most of the time, the resulting sorbitan mixture is not isolated or even separated into the individual anhydrosugars, but is processed directly into isosorbide or sorbitan esters.
properties
1,4-Sorbitan is described in the literature as a (colorless) solid with a melting point of 111-112 ° C. after decolorization and recrystallization from isopropanol. In industrial syntheses, the mixture of isomers is obtained as a dark oil. Sorbitan dissolves in water and lower alcohols.
use
1,4-Sorbitan is used as the starting material for isosorbide and for sorbitan fatty acid esters , which are lipophilic non-ionic surfactants . Because of their high interfacial activity , sorbitan fatty acid esters (under the trade name Span ) are used as biodegradable emulsifiers , solubilizers and stabilizers in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations as non-toxic formulation auxiliaries in a variety of applications from coatings to cleaning, crop protection and foodstuffs, as well as temperature and UV-stable plasticizers for PVC .
Reaction with ethylene oxide results in the corresponding ethoxylated sorbitan fatty acid esters from the chips , which form a class of hydrophilic non-ionic emulsifiers under the trade name Tween .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Patent US2390395 : Sorbitan and process for making the same. Published December 4, 1945 , Applicant: Atlas Powder Co, Inventor: Soltzberg Sol.
- ↑ a b c Patent US7649099 : Method of forming a dianhydrosugar alcohol. Published January 19, 2010 , Applicants: Battelle Memorial Institute, Inventors: Johnathan E. Holladay, Jianli Hu, Yong Wang, Todd A. Werpy, Xinjie Zhang.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b A. Yamaguchi et al .: Sorbitol dehydration in high temperature liquid water. In: Green Chem . 2011, 13, pp. 873-881, doi: 10.1039 / C0GC00426J
- ↑ Patent US20090259057 : Dianhydrosugar production process. Published October 15, 2009 , Inventors: David James Schreck, Marion McKinley Bradford, Nye Atwood Clinton, Paul Aubry.
- ↑ J. Smidrkal et al .: Two stage synthesis of sorbitan esters, and physical properties of the products. In: Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 106 (12), 2004, pp. 851-855, doi: 10.1002 / ejlt.200401003 .
- ↑ Patent US20070173653 : Method of performing sugar dehydration and catalyst treatment. Published on July 26, 2007 , Inventors: Jianli Hu, Johnathan Holladay, Xinjie Zhang, Yong Wang.
- ^ Span and Tween
- ↑ Patent US6362353 : Manufacturing of fatty acid esters as surfactants. Published March 26, 2002 , Applicant: Imperial Chemical Industries, PLC, Inventor: James Morgan Hunter Ellis, Jeremy James Lewis, Roger James Beattie.