19P / Borrelly
| 19P / Borrelly [i] | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Properties of the orbit ( animation ) | |
| Orbit type | short period |
| Numerical eccentricity | 0.624 |
| Perihelion | 1.355 AU |
| Aphelion | 5.861 AU |
| Major semi-axis | 3.608 AU |
| Sidereal period of rotation | 6 a 311 d |
| Inclination of the orbit plane | 30.324 ° |
| Perihelion | July 22, 2008 |
| Orbital velocity in the perihelion | 32.61 km / s |
| Physical properties of the core | |
| Medium diameter | 8 × 4 × 4 km |
| Dimensions | 3.3 x 10 13 kg |
| Medium density | 0.49 g / cm³ |
| Albedo | 0.029 ± 0.006 |
| story | |
| Explorer | ALN Borrelly |
| Date of discovery | December 28, 1904 |
| Older name | 1905 II, 1904e |
| Source: Unless otherwise stated, the data comes from JPL Small-Body Database Browser . Please also note the note on comet articles . | |
The comet Borrelly (official designation 19P / Borrelly ) is a short-period comet , by the on September 22, 2001 NASA - space probe Deep Space 1 was explored.
discovery
The comet was discovered on December 28, 1904 by Alphonse Louis Nicolas Borrelly in the constellation Whale . Soon after, the comet was recognized as having a short period, and its return for 1911 was correctly predicted.
Orbit
Borrelly runs in an elliptical orbit around the sun, whose closest point to the sun ( perihelion ) lies just inside the orbit of Mars . The point furthest from the sun ( aphelion ) lies slightly outside the orbit of the planet Jupiter , which distinguishes it as a short-period comet of the Jupiter family .
Deep Space 1 space probe
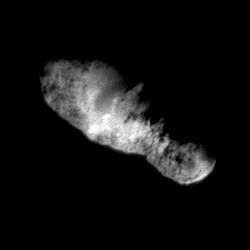
On September 22, 2001, NASA's Deep Space 1 spacecraft flew past the comet at a distance of 2,200 km. Borrelly was the fourth comet after Giacobini-Zinner , Halley and Grigg-Skjellerup to be explored by a spacecraft, and the second (after Halley) to be able to transmit images of the core to Earth. This appeared in the pictures as an elongated structure with a size of about 8 × 4 × 4 km. The density of the core is only 0.49 g / cm³. Its surface is the darkest in the solar system known to date: the average albedo is 0.03, making it as dark as black toner powder . This makes it the darkest object in the solar system. Some particularly black spots even have a reflectance value of 0.007, for which hardly any minerals are known up to now.
See also
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Darkest object in the Solar System. Retrieved July 15, 2021 (German).