Azirine
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||
| Surname | Azirine | ||||||||||||
| other names |
2 H azirine |
||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 3 N | ||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 41.05 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||
Azirine , more precisely 2 H -azirine , is the simplest unsaturated nitrogen - containing three - membered heterocycle . It belongs to the heterocyclic parent systems and to the substance class of cyclic imines . The saturated analog is aziridine , the carbocyclic analog is cyclopropene . The isomeric 1 H -azirine, which carries the proton on the nitrogen atom, is not stable and isomerizes to 2 H -azirine.
Manufacturing
The preparation of 2 H -azirine can be obtained from vinyl azide at reduced pressure and elevated temperature. Acetonitrile and ketenimine are formed as by-products .
properties
The absorption maximum in pentane is in the ultraviolet range at a wavelength of λ = 229 nm .
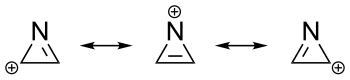
The azirine cation is the smallest heterocyclic aromatic compound.
Reactions
Azirine is very reactive due to its high ring tension . It reacts with electrophiles and nucleophiles with ring opening.
Azirine derivatives arise as intermediates in the Neber rearrangement .
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ a b J.-C. Guillemin, J.-M. Denis, M.-C. Lasne, J.-L. Ripoll in: Tetrahedron 1988, 44 (14), 4447-4456. doi : 10.1016 / S0040-4020 (01) 86146-9
