Benzylaminopurine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
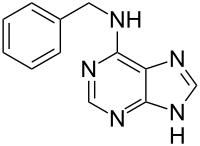
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Benzylaminopurine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 12 H 11 N 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 225.25 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
229-233 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Benzylaminopurine or benzyladenine , or BAP for short , is a synthetic phytohormone that is used in cell and tissue culture .
For the first time, BAP was synthesized and examined in the laboratory of the Swedish plant physiologist Folke Karl Skoog .
In 2010 the EU carried out a risk assessment of the substance.
It belongs to the first generation of synthetically produced cytokinins and has a positive influence on plant growth. BAP influences flower and fruit formation by stimulating the rate of cell division .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h Data sheet 6-Benzyladenine, 99% from AlfaAesar, accessed on December 26, 2019 ( PDF )(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ Vladimir Sidorov, Larry Gilbertson, Prince Addae, David Duncan: Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of seedling-derived maize callus . In: Plant Cell Reports . tape 25 , no. 4 , April 2006, p. 320–328 , doi : 10.1007 / s00299-005-0058-5 ( PDF ).
- ↑ M. Ahmadabadi, S. Ruf et al: A leaf-based regeneration and transformation system for maize (Zea mays L.). In: Transgenic Research. 16 (4), 2007, pp. 437-448.
- ↑ NJ Leonard, WJ Burrows, F. Skoog: Isolation and identification of cytokinins located in the transfer ribonucleic acid of tobacco callus grown in the presence of 6-benzylaminopurine . In: Biochemistry . tape 10 , no. June 12 , 1971, p. 2189-2194 , doi : 10.1021 / bi00788a002 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance 6-benzyladenine. In: European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Journal. 8 (10), 2010, p. 1716.
