Lead telluride
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
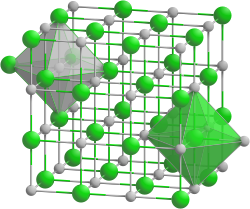
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Pb 2+ __ Te 2− | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Lead telluride | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | PbTe | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
gray solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 334.80 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
8.164 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
905 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
almost insoluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Lead telluride is an inorganic chemical compound of lead from the group of tellurides .
Occurrence
Lead telluride occurs naturally in the form of the mineral altaite .
Extraction and presentation
Lead telluride can be obtained by reacting lead with tellurium or a boiling solution of lead (II) salts with tellurium powder.
properties
Lead telluride is a gray, brittle crystalline solid that is insoluble in water. It is a semiconductor and has the cubic sodium chloride structure with the space group Fm 3 m (space group no. 225) .
use
Lead telluride is used as a thermocouple in a temperature range of 200 to 600 ° C.
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Paperback for chemists and physicists . Springer DE, 1997, ISBN 3-540-60035-3 , pp. 666 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Lead (II) telluride, 99.998% trace metals basis at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 20, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b David R. Lide: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . CRC Press, 2012, ISBN 1-4398-8049-2 , pp. 4–71 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b José S. Casas, José Sordo: Lead: Chemistry, analytical aspects, environmental impact and health effects . Elsevier, 2006, ISBN 0-444-52945-4 , pp. 31 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Christine Junior: Analysis of thermoelectric modules and overall systems . BoD - Books on Demand, 2010, ISBN 3-89936-987-4 , pp. 107 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ Terry M. Tritt: Thermal Conductivity: Theory, Properties, and Applications . Springer, 2005, ISBN 0-306-48327-0 , pp. 128 ( limited preview in Google Book search).


