Cesium azide
| Crystal structure | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
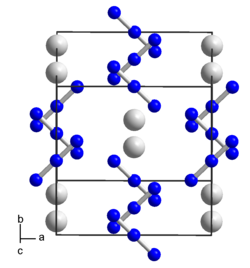
|
||||||||||||||||
| __ Cs + __ N 1 / 3− | ||||||||||||||||
| Crystal system |
tetragonal |
|||||||||||||||
| Space group |
I 4 / mcm (No. 140) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lattice parameters |
a = 6.5412 Å, c = 8.0908 Å |
|||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cesium azide | |||||||||||||||
| Ratio formula | CsN 3 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 174.93 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
3.5 g cm −3 (25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
310 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
390 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Cesium azide is an inorganic chemical compound of cesium from the group of azides .
Extraction and presentation
Caesiumazid, by reaction of hydrogen azide and cesium are obtained.
It can also be obtained by reacting cesium carbonate with hydrazoic acid.
properties
Cesium azide is a solid. It crystallizes in a tetragonal crystal structure with the space group I 4 / mcm (space group no. 140) and four formula units per unit cell .
use
Cesium azide can be used to make high purity cesium.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Ulrich Müller: Refinement of the crystal structures of KN 3 , RbN 3 , CsN 3 and TlN 3 . In: Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry . tape 392 , no. 2 , 1972, p. 159-166 , doi : 10.1002 / zaac.19723920207 .
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet Cesium azide, 99.99% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 18, 2013 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b c d Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler a . a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 458.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Inorganic Compounds, pp. 4-57.
- ^ CC Addison: Inorganic Chemistry of the Main-Group Elements . Royal Society of Chemistry, 1974, ISBN 0-85186-762-6 , pp. 54 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ FRITZ BLATTER and ERNST SCHUMACHER: PRODUCTION OF HIGH PURITY CAESIUM , Journal of the beg-Common Metals, 115 (1986) 307-313


