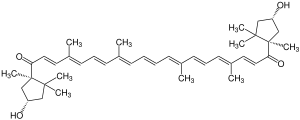
Capsorubin
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Capsorubin | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 40 H 56 O 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
purple-red solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 600.87 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.016 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
201 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Capsorubin is one of the xanthophylls (oxygen-containing carotenoids ), it is a natural substance and one of the tetraterpenes . A system of conjugated double bonds absorbs light and gives the capsorubin a bright red color. The dye is used in the manufacture of food and cosmetics for coloring.
Occurrence
Natural sources of capsorubin are red peppers , nightshade family or lilies . The amount of capsorubin in paprika extract, which was obtained from Spanish pepper , for example , is 7% of all carotenoids. It is the third most common carotenoid, followed by capsanthin with 37% and zeaxanthin with 8%.
use
Capsorubin, together with capsanthin , is part of paprika extract. This is carried under the designation E 160c in the food industry. It is used to color or flavor food red. Since there are no quantity restrictions in many areas of application, it can be used for many areas. Application examples are chips, drinks, jam, cheese, ice cream or soups.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on E 160c: Paprika extract, capsanthin, capsorubin in the European database for food additives, accessed on June 16, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d E. Jucker, P. Karrer: Carotenoids. Springer, Basel 1948, pp. 258-259.
- ↑ a b Capsorubin. World of Chemicals, accessed August 26, 2017 .
- ↑ Capsorubin. ChemSrc, accessed August 26, 2017 .
- ↑ L. Zechmeister: In: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 1935, pp. 30-45.
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ Hoffmann La-Rouche, Co .: Carotenoids. Jumper. Basel 1971, p. 20.
- ↑ Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of paprika extract (E 160c) as a food additive. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Parma, Italy 2017, p. 29, doi: 10.2903 / j.efsa.2015.4320 .
- ↑ Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of paprika extract (E 160c) as a food additive. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), Parma, Italy 2017, pp. 11–12, doi: 10.2903 / j.efsa.2015.4320 .
- ↑ D. Hahne: E numbers, additives: All E numbers explained and evaluated. Stiftung Warentest, 2017, ISBN 978-3-86851-451-3 , pp. 18-19.
- ↑ G. Lehmann, B. Binkel (Ed.): Identification of dyes in cosmetics. VCH Verlagsges., Weinheim 1986.

