Quinolinate phosphoribosyl transferase
| Quinolinate phosphoribosyl transferase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 297 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Homodimer | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | QPRT | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 2.4.2.19 , glycosyl transferase | |
| Response type | Transfer of a ribosyl residue | |
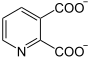
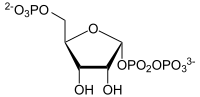
| Substrate | Quinolinate + α-D-5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate | |
| Products | Nicotinate D-ribonucleotide + PP i + CO 2 | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Homology family | QPRT | |
| Parent taxon | Bacteria, fungi, animals | |
In quinolinate phosphoribosyltransferase (QPRT) is the enzyme that the transfer of a, ribose molecule to quinolinic acid catalyzed . This reaction is a partial step in the biosynthesis of NAD + , an important coenzyme . QPRT is found in bacteria , animals, and some fungi. In humans it is mainly localized in the liver , kidneys , heart and adrenal glands and is greatly increased in some tumor cell lines.
Catalyzed reaction
α-D-5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PPRP) is transferred to quinolinate with splitting off of carbon dioxide, and nicotinate-D-ribonucleotide and diphosphate are formed. In rats, the reaction takes place mainly in the liver.
Individual evidence
- ↑ UniProt Q15274
- ↑ BioGPS entry
- ↑ Fukuwatari T, Morikawa Y, Hayakawa F, Sugimoto E, Shibata K: Influence of adenine-induced renal failure on tryptophan-niacin metabolism in rats . In: Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry . 65, No. 10, October 2001, pp. 2154-61. PMID 11758903 .
Web links
Wikibooks: Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry: Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism - Learning and Teaching Materials