Chronotype
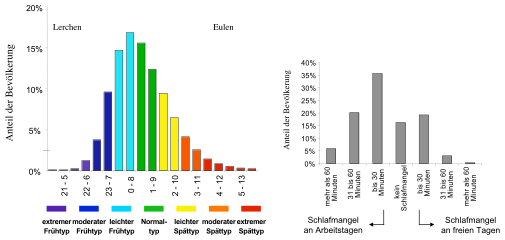
right: lack of sleep on working days or on days off.
In chronobiology, chronotypes are the categories of people who, based on the internal biological clock (day / night), have physical characteristics such as B. Hormone levels, body temperature, sleeping and waking phases, ability to perform at different times of the day to different degrees.
Influencing the day-night rhythm
In humans and other mammals, the hormone melatonin , which controls the day-night rhythm, is formed in the retina , pineal gland and intestine . The control of the pineal gland is u. a. located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus , which is located in the hypothalamus . There is evidence that different pacemakers have different effects on people's sleep phases. The synchronization with the astronomical day-night change takes place via the excitation of the photosensitive ganglion cells in the retina, whose maximum light sensitivity is at 480 nm wavelength and thus in the blue.
Main categories
As can be seen from the colorful bar chart of the Center for Chronobiology at the Institute for Medical Psychology at LMU (above), the frequency distribution in the population as a function of bedtime (and thus the chronotype) results in an approximately normal distribution (bell curve) , as is the case with the Distribution of shoe sizes or body sizes is the case. The colorful graphic shows that the left ascending leg of the normal distribution curve includes the early risers (“larks”), the area around the high point of the curve includes the normal type and the right descending leg includes the late risers (“owls”). The left leg of the curve is shorter and climbs faster. The right thigh is overall longer and descends more moderately. The Center for Chronobiology distinguishes between seven chronotypes: purple: "extreme early type", blue: "moderate early type", light blue: "light early type", green: "normal type", yellow: "slight late type", orange: "moderate late type" and red: "extreme late type". The right gray bar graph shows the proportion of the population as a function of lack of sleep .
If the chronotypes are divided into three main types, the following simplified system arises: 1. Early riser (“lark”; purple and blue in the graphic) ; 2. Normal type (light blue and green) , who makes up the majority of the population, and 3. Late risers (“owl”, “evening type”, “evening person”, “night person”, “late rhythmist”; yellow, orange and red) who follow the normal type is more common than the early riser type.

The chronotype is basically genetically designed, but changes with age: small children are almost always larks. In puberty and adolescence, the individual chronotype develops very quickly in the late direction and reaches an extreme at 19.5 (female) and 20.9 (male) years at an average of 4:45 and 5:30 in the middle of the undisturbed Sleep period ( local time ). At this age, the development suddenly turns in the opposite direction. At the age of around 55, the gender-specific difference disappears at an average of 3:30 a.m. in the middle of the undisturbed sleep period.
A sustainable adaptation of the sleeping times to the social environment or professional requirements is only possible to a very limited extent using lighting technology (morning light exposure with high color temperature and sufficient illuminance, i.e. very bright blue light).
literature
- Jennifer Ackerman: 24 hours: A day in the life of your body. Rowohlt, Reinbek 2009, ISBN 978-3498000783 .
- Peter Spork : The clockwork of nature. Rowohlt, Reinbek 2004, ISBN 3-499-61665-3 .
- Peter Spork: The sleep book. Rowohlt, Reinbek 2007, ISBN 3498063871 .
- Peter Spork : Wake up! Departure to a good rested society. Carl Hanser Verlag, Munich 2014, ISBN 978-3-446-44051-7 .
- Till Roenneberg et al .: A marker for the end of adolescence. In: Current Biology. Volume 14, No. 24, 2004, pp. R1038 – R1039, doi : 10.1016 / j.cub.2004.11.039 - on the age dependence of the chronotype.
Web links
- delta-t club for late people
- Till Roenneberg: Social Jetlag and Obesity (video abstract)
- The early bird doesn't always catch the worm. Young people tend to have worms early in the morning. Telepolis , January 1, 2005.
- Why owls become smokers. Chronic chronobiological jet lag increases drug use. Telepolis, March 30, 2006.
- Institute for Medical Psychology, Working Group for Medical Chronobiology, LM University of Munich
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b graphic: Frequency of different chronotypes in the (German) population. LMU , Institute for Medical Psychology, Center for Chronobiology , 2010. Left graphic: Frequency of the different sleep times (eg "0–8" means: the person sleeps on average from midnight to 8 am); Right graphic: lack or excess of sleep on working days compared to days off.
- ↑ purple: "extreme early type", blue: "moderate early type"
- ↑ light blue: "light early type", green: "normal type"
- ↑ yellow: "slight late type", orange: "moderate late type", red: "extreme late type"