Cnicin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
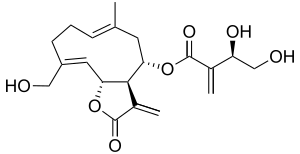
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Cnicin | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
[(1 R , 2 S , 4 E , 8 Z , 10 S ) -8- (hydroxymethyl) -4-methyl-13-methylidene-12-oxy-11-oxabicyclo [8.3.0] trideca-4,8- dien-2-yl] (3 S ) -3,4-dihydroxy-2-methylidene-butanoate |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 20 H 26 O 7 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless and odorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 378,42 g · mol -1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
142-143 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
little in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Cnicine is an unsaturated sesquiterpene dihydroxylactone that is esterified with a substituted acrylic acid.
Occurrence
Cnicin belongs to the germacranolide group and is formed in higher concentrations in Benedictine herb ( Cnicus benedictus ) or in panicle knapweed ( Centaurea stoebe ).
The highest and lowest concentrations are found in the leaves (0.86–3.86% cnicine) and in the trunk, respectively.
effect
The effect of the cnicin is used in the context of phytotherapy . As an effective ingredient in Benedictine herb, it stimulates gastric juice production and is effective against digestive problems. Benedictine herb is used in the form of tea infusions or alcoholic extracts .
toxicology
A high dose of cnicin has acute toxic effects in experiments with rats and mice. Furthermore, an overdose of Cnicin can lead to severe irritation in the throat, pharynx and esophagus. Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract up to nausea, cramps, vomiting and diarrhea, accompanied by a fever, are possible.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Cnicin data sheet (PDF) from Carl Roth , accessed on May 7, 2018.
- ↑ a b University of Düsseldorf, Biology Didactics, Leaf Spices: Cnicin , accessed on December 29, 2013.
- ↑ M. Cheeseman: Providing Supplement, with or without PEG, to reduce the effects of cnicin and enhance grazing of spotted knapweed by sheep and cattle , Masters Thesis, Montana State University, 2006.
- ^ Association for Medicinal and Spice Plants SALUPLANTA eV Bernburg: Handbook of Medicinal and Spice Plant Cultivation. Volume 1, self-published, 2009, ISBN 978-3-935971-54-6 .
- ↑ Eberhard Nürnberg, Peter Surmann (Ed.): Hager's handbook of pharmaceutical practice. Volume 2, 5th edition. Springer, Berlin 1991, ISBN 3-540-61618-7 .

