Combretastatin A-4
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
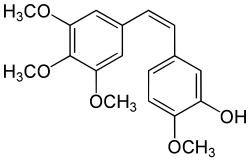
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Combretastatin A-4 | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 18 H 20 O 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 316.35 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in DMSO (> 10 g l −1 ) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Combretastatin A-4 is a natural substance from the stilbene group . It was first discovered and isolated from Combretum caffrum , a type of South African long filament .
Occurrence
Natural combretastatins are found in the African tree Combretum caffrum . Plants synthesize combretastatin and other stilbenes as defense substances via the shikimic acid route via phenylalanine and malonyl-CoA . The last step in biosynthesis is catalyzed by the enzyme stilbene synthase. Chemically speaking, they are stilbenoids, as the structures are derived from stilbene (1,2 ‑ diphenylethene). There are several naturally occurring derivatives, the best known and most biologically active representative being combretastatin A-4. The low water solubility of 350 µM is a disadvantage for pharmaceutical formulations.
effect
Combretastatin A-4, like the alkaloid colchicine, is an inhibitor of tubulin polymerization that destabilizes microtubules and binds them in a pocket between the α and β subunits of tubulin. This pocket is therefore referred to in the literature as the “colchicine binding site”. Fosbretabulin , a phosphoric acid ester of combretastatin A-4, is currently (2019) in a phase II clinical trial due to its antitumor activity. In laboratory tests an effect of combretastatin A-4 against dengue and Zika viruses could also be shown.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Combretastatin A4, ≥98% (HPLC), powder from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on December 11, 2019 ( PDF ).
- ↑ GR Pettit, SB Singh, E. Hamel, CM Lin, DS Alberts: Isolation and structure of the strong cell growth and tubulin inhibitor combretastatin A-4 . In: Experientia . tape 45 , no. 2 , February 1989, ISSN 0014-4754 , pp. 209-211 , doi : 10.1007 / BF01954881 .
- ↑ Philippe Jeandet, Bertrand Delaunois, Alexandra Conreux, David Donnez, Vitale Nuzzo: Biosynthesis, metabolism, molecular engineering, and biological functions of stilbene phytoalexins in plants . In: BioFactors . tape 36 , no. 5 , 2010, ISSN 1872-8081 , p. 331-341 , doi : 10.1002 / biof.108 .
- ↑ Lauren Lee, Lyda M. Robb, Megan Lee, Ryan Davis, Hilary Mackay: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluations of 2,5-Diaryl-2,3-dihydro-1,3,4-oxadiazoline Analogs of Combretastatin-A4 . In: Journal of Medicinal Chemistry . tape 53 , no. 1 , January 14, 2010, ISSN 0022-2623 , p. 325–334 , doi : 10.1021 / jm901268n , PMID 19894742 , PMC 2810428 (free full text).
- ^ Roberto Gaspari, Andrea E. Prota, Katja Bargsten, Andrea Cavalli, Michel O. Steinmetz: Structural Basis of cis- and trans-Combretastatin Binding to Tubulin . In: Chem . tape 2 , no. 1 , January 12, 2017, ISSN 2451-9294 , p. 102–113 , doi : 10.1016 / j.chempr.2016.12.005 .
- ↑ Karol Jaroch, Maciej Karolak, Przemysław Górski, Alina Jaroch, Adrian Krajewski: Combretastatins: In vitro structure-activity relationship, mode of action and current clinical status . In: Pharmacological Reports . tape 68 , no. 6 , December 1, 2016, ISSN 1734-1140 , p. 1266–1275 , doi : 10.1016 / j.pharep.2016.08.007 .
- ↑ Michael Richter, Mila M. Leuthold, Dominik Graf, Ralf Bartenschlager, Christian D. Klein: Prodrug Activation by a Viral Protease: Evaluating Combretastatin Peptide Hybrids To Selectively Target Infected Cells . In: ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters . tape 10 , no. 8 , August 8, 2019, ISSN 1948-5875 , p. 1115-1121 , doi : 10.1021 / acsmedchemlett.9b00058 , PMID 31413794 , PMC 6691480 (free full text).

