Direct dyes
Nouns or direct dyes are dyes for cellulose and regenerated cellulose , for example cotton , jute , viscose or paper , which, in contrast to reactive dyes, are only bound to the fiber through physical interactions ( van der Waals forces ) and consequently have a high affinity for the substrate must own.
Chemical constitution
The direct dyes mainly come from the group of azo dyes , only a few dioxazine dyes , phthalocyanine dyes and non-azo metal complex dyes have a certain significance. For the required high substantivity , the dye molecules must have a coplanar structure and have long chains of conjugated double bonds .
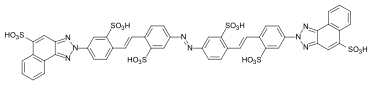
Dyes with a high substantivity are, for example, azo dyes with 3,3'-disubstituted benzidine derivatives as diazo components :
CI Direct Blue 8
azo dye with 3,3'-dimethoxybenzidine as a diazo component.
Despite the good substantive properties, these dyes are no longer used due to the carcinogenic properties of benzidine and various benzidine derivatives. Since the azo dyes produced from 2,2'-disubstituted benzidine derivatives do not have a coplanar structure due to steric hindrance , they are not sufficiently substantive and are not suitable as direct dyes.
Dyes with a urea structure show good substantivity . The reaction of aromatic amines with phosgene gives symmetrical diaryl urea derivatives which, as coupling components, react with a diazo component to form a disazo dye.
Example:
By reacting I-acid 1 with phosgene 2 , the intermediate I-acid-urea 3 is obtained . This couples with diazonium salt 5 , which is obtained by the diazotization of aniline 4 , to form the direct dye CI Direct Orange 26 6 .
Synthesis of CI Direct Orange 26 (azo dye with a urea bridge).
Direct staining
In direct dyeing, the substrate to be dyed is placed in an aqueous solution of the direct dyes, the so-called dye liquor . The high affinity of the dyes means that they are usually absorbed directly onto the fiber (hence the name direct dyes ). The proportion of the dye in the dyed material to that in the liquor, the so-called exhaustion rate , can be influenced by adding salt and / or changing the pH value. Good noun dyes with a high substantivity achieve a degree of exhaustion of> 99%, i.e. H. the dye liquor is almost colorless after dyeing.
The advantage of direct dyes is their very simple dyeing process, while their disadvantages are the significantly poorer wet fastness compared to reactive dyes: noun-dyed textiles can still "bleed" after being washed several times and thus rub off on other textiles that have been washed.
Examples
CI name CI no. CAS no. other names structure colour Direct Yellow 1 22250 6472-91-9 Chrysamine G. Direct Yellow 9 19540 1829-00-1 Thiazole yellow Direct Yellow 7
Direct Yellow 5949010 8064-60-6 Primulin Direct Yellow 11 40000 Direct Yellow R. Direct Yellow 12 24895 2870-32-8 Chrysophenine Direct Yellow 27 13950 10190-68-8 Direct Fast Yellow 5GL Direct Yellow 28 19555 8005-72-9 Chloramine yellow Direct Yellow 44 29000 8005-52-5 Direct Fast Yellow L4G Direct Yellow 50 29025 3214-47-9 Direct Fast Yellow RS Direct Yellow 86 29325 50925-42-3 Direct Fast Yellow RL Direct Yellow 96 61725-08-4 Direct Fluorescent Light Yellow 7GFF
Diphenyl Brilliant FlavinDirect Yellow 106 40300 12222-60-5 Direct Fast Yellow L3R Direct Yellow 120 29040 12222-63-8 Direct Fast Yellow GR Direct Yellow 142 71902-08-4 Direct Fast Yellow PG Direct Yellow 147 Direct Fast Yellow GL Direct Orange 26 29150 3626-36-6 Direct Orange S Direct Orange 34 40220 12222-37-6 Direct Fast Orange 7GL Direct Orange 39 40215 1325-54-8 Direct Light Fast Orange 4GL Direct Brown 1 30045 3811-71-0 Direct Brown D3G Direct Brown 2 22311 2429-82-5 Direct Brown M / MM Direct Brown 210 22312 12222-29-6 Direct Fast Brown GTL Direct Red 2 23500 992-59-6 Benzopurpurine Direct Red 13 22155 1937-35-5 Direct Red B
Direct BordeauxDirect Red 16 27680 6227-02-07 Direct Light Fast Red 6B Direct Red 28 22120 573-58-0 Congo red 
Direct Blue 1 24410 2610-05-1 Chicago
blue 6B diamine pure blue FFDirect Blue 6 22610 2602-46-2 Direct Blue 2BA Direct Blue 14 23850 72-57-1 Trypan
Blue 3B Benzamine BlueDirect Blue 71 34149 4399-55-7 Sirius Blue S-BRR Direct Blue 199 74190 12222-04-7 Direct Blue FBL Direct Green 1 30280 3626-28-6 Direct dark green Direct Green 6 30295 4335-09-5 Direct Green B Direct Black 38 30235 1937-37-7 Direct deep black E. CAS-No .: Na salt / structures: free acid
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Hans Beyer, Wolfgang Walter: Textbook of organic chemistry . 18th edition. S. Hirzel Verlag, Stuttgart 1978, ISBN 3-7776-0342-2 , p. 517-519 .
- ^ H. Bach, E. Pfeil, W. Philippar, M. Reich: Molecular structure and adhesion of substantive dyes on cellulose . In: Angewandte Chemie . tape 75 , no. 9 , May 7, 1963, pp. 407-416 , doi : 10.1002 / anie.19630750903 .
- ^ A b Klaus Hunger (Ed.): Industrial Dyes: Chemistry, Properties, Applications . WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 978-3-662-01950-4 , p. 158 ff . ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to CI Direct Blue 8 : CAS number: 2429-71-2, EC number: 219-382-7, ECHA InfoCard: 100.017.621 , PubChem : 17055 , ChemSpider : 16735697 , Wikidata : Q27254953 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links for I-acid urea : CAS number: 134-47-4, EC number: 205-142-9, ECHA InfoCard: 100.004.676 , PubChem : 67254 , ChemSpider : 60588 , Wikidata : Q27074444 .
- ↑ External identifiers or database links to CI Direct Orange 26 (di-sodium salt) : CAS number: 3626-36-6, EC number: 222-838-8, ECHA InfoCard: 100.020.763 , PubChem : 77182 , ChemSpider : 21171947 , Wikidata : Q72469576 .