Metal complex dyes
Metal complex dyes are coordination compounds of a metal ion with one or more dye ligands that have electron donor groups.
In the case of the metal complex dyes, the copper and chromium compounds predominate . To a lesser extent, however, cobalt , nickel and iron complexes are also used as metal complex dyes. The ligands are often multidentate azo dyes , azomethine dyes , formazans or phthalocyanines .
Metal complex dyes are characterized by very good lightfastness .
history
The stain dyeing already practiced in the Middle Ages is an example of the use of metal complex dyes. The dyed material is impregnated with a solution of aluminum , iron, chromium or tin salts and then dyed with natural dyes that contain a chelate system (e.g. alizarin from the roots of the madder dyer's head ). The mostly water-insoluble metal complex forms on the fiber.
The first metallizable synthetic dyes were developed at the end of the 19th century. The first representative from the class of azo dyes was CI Mordant Orange 1 ( Alizarin Yellow ), which was synthesized in 1887 by Rudolf Nietzki . The synthesis of the metallizable 2,2'-dihydroxyazo dyes followed in 1893 and in 1912 the synthesis of the first previously metallized 1: 1 chromium complex dyes ( René Bohn , BASF ), which were marketed from 1920 (BASF, Ciba ). Further milestones were the first synthesis of copper phthalocyanine (1927), the development of water-soluble 1: 2 chromium complexes without sulfo groups (1949), the development of asymmetrical 1: 2 metal complex dyes with only one sulfo group (1962) and of 1: 2 chromium complexes with two sulfo groups (1970).
The commercially important post-chrome plating process was developed as early as the 1940s. The fiber is first colored with a metalizable dye and then treated with sodium or potassium dichromate so that the chromium complex dyes are formed directly on the fiber. This process is used in particular when dyeing wool in dark shades (example: Mordant Black 9).
Azo / azomethine complex dyes
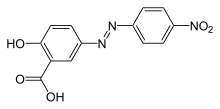
The most important metal complex dyes from the class of azo dyes or azomethine dyes contain a 2,2'-dihydroxy, a 2-carboxy-2'-hydroxy or a 2-amino-2'-hydroxy-substituted azo compound, or a 2,2'-dihydroxy or 2-carboxy-2'-hydroxy substituted azomethine compound:
Azo dyes with 2,2'-dihydroxy, 2-carboxy-2'-hydroxy, 2-amino-2'-hydroxy substituents Azomethine dyes
with 2,2'-dihydroxy, 2-carboxy-2'-hydroxy substituents
The aromatic nuclei are benzene , naphthalene or pyrazolone derivatives. These compounds act as tridentate ligands. Thus the Cu 2+ ion with the coordination number 4 can form complexes with a dye ligand of this type. The fourth coordination site is occupied by a solvent molecule. Cr 3+ with the coordination number 6 forms complexes with two dye ligands, so-called 2: 1 complexes.
Copper complex dyes
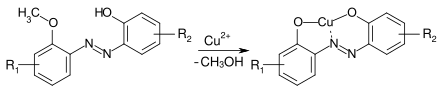
The copper complex dyes are produced from 2,2'-dihydroxyazo dyes under mild conditions by reaction with copper salts (e.g. CuSO 4 ) at pH 4-7 in the presence of sodium acetate as a buffer . However, 2,2'-dihydoxyazo dyes are sometimes difficult to obtain because the corresponding o -hydroxydiazonium salts are relatively inert. The following variants offer an alternative access to the corresponding Cu complex dyes:
- Dealkylative coppering: When 2-alkoxy-2'-hydroxy-azo dyes are converted at a temperature> 80 ° C (possibly also at T> 100 ° C under pressure), the Cu complex is formed with cleavage of the alkoxy group . As a rule, the methoxy compounds are used.
- Oxidative coppering: When an o -hydroxyazo dye is reacted with an oxidizing agent such as H 2 O 2 in the presence of copper (II) ions, the 2,2'-dihydroxyazo dye-Cu complex is also obtained.
- Starting from a 2-chloro-2'-hydroxy dye, the copper complex dye is obtained by reaction with a copper salt in an alkaline medium at 50.degree.
Examples
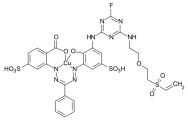
Formazan dyes
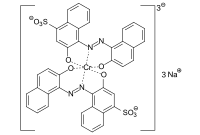
The formazan dyes, which are structurally related to the azo dyes, are 1,5-diaryl or 1,3,5-triaryl-substituted derivatives of the hypothetical parent compound NH = N ‑ CH = N ‑ NH 2 - formally a hydrazone substituted with an azo group . These were first described in 1892 by Hans von Pechmann and Eugen Bamberger . The simplest representative of the 1,3,5-aryl-substituted formazans is triphenylformazan . The formazans form complexes with various metal ions (copper, nickel, cobalt), the unsubstituted di- and triarylformazanes being bidentate. By introducing electron donor groups (hydroxyl, carboxy, amino groups) into the o -position of the aryl groups in the 1- and 5-positions, tridentate and tetradentate ligands are obtained.
The tetradentate 1,3,5-triaryl-substituted copper formazan complexes are essentially of commercial interest. An important representative is a triphenylcupperformazan in which the phenyl group in the 1-position is substituted with a hydroxyl and amino group and the 5-phenyl group in the 5-position with a carboxy group.
Additional sulfo groups increase the water solubility of the compound. By derivatizing the amino group, for example with trichlorotriazine or trifluorotriazine , various formazans from the class of reactive dyes can be obtained .
Manufacturing
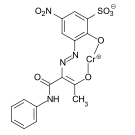
Benzaldehyde ( 1 ) reacts with 2-carboxy-5-sulfo-phenylhydrazine ( 2 ) to form the hydrazone ( 3 ). In the presence of copper sulfate, the hydrazone couples with diazotized 6-acetylamino-4-sulfo-2-aminophenol ( 4 ) to give the copper formazan compound ( 6 ). The copper formazan chromophore ( 7 ) is obtained by alkaline hydrolysis of the acetylamino group .
Examples
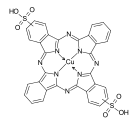
Phthalocyanine dyes
The phthalocyanine dyes, metal complexes of phthalocyanine substituted with solubilizing groups, such as -SO 3 H . Phthalocyanine forms stable complexes with a large number of metals and semi-metals . Of commercial importance, however, are primarily the copper complexes and, to a lesser extent, the nickel complexes. Important intermediate stages in the production of copper phthalocyanine dyes are the sulfonic acid chlorides , which are obtained from the reaction of copper phthalocyanine with chlorosulfonic acid and thionyl chloride at temperatures> 100 ° C. The sulfochlorides can be converted to sulfonamides with aromatic or aliphatic amines . Sulfonic acids are obtained by hydrolysis of the sulfochloride groups.
Depending on the metal ion and the substituents, turquoise to brilliant green shades are available with the phthalocyanine dyes. The phthalocyanine dyes are characterized by excellent stability and high lightfastness.
Examples
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c Klaus Hunger (Ed.): Industrial Dyes: Chemistry, Properties, Applications . WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 978-3-662-01950-4 , p. 85 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Entry on metal complex dyes. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on March 25, 2019.
- ^ Heinrich Zollinger: Color Chemistry: Syntheses, Properties, and Applications of Organic Dyes and Pigments . 3. Edition. WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2003, ISBN 3-906390-23-3 , p. 206 ff . ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Max Hungerbühler: About the demethylating coppering of o-methoxy-o'-oxy dyes . Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, Zurich 1949, doi : 10.3929 / ethz-a-000103794 .
- ^ R. Price: The Chemistry of Metal Complex Dyestuffs . In: K. Venkataraman (Ed.): The Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes . tape III . Academic Press, New York, London 1970, ISBN 0-12-717003-0 , pp. 373 ff .
- ↑ H. v. Pechmann: About the so-called. mixed azo compounds . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . tape 25 , no. 2 , July 1892, p. 3190 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.189202502174 .
- ↑ Eug. Bamberger, E. Wheelwright: About the action of diazobenzene on acetoacetic ether . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . tape 25 , no. 2 , July 1892, p. 3201 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.189202502175 .
- ↑ a b Patent DE3705789 : Copper complex formazan compounds, process for their production and their use as dyes. Published on September 1, 1988 , inventors: Günther Schwaiger, Hartmut Springer, Werner Russ.
- ↑ G.Booth: Phthalocyanines . In: K. Venkataraman (Ed.): The Chemistry of Synthetic Dyes . tape V . Academic Press, New York, London 1971, pp. 241 ff .