Coordination number
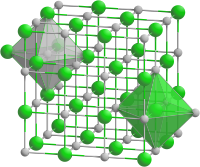
The coordination number (KZ) denotes the number of the closest neighbors of a structural unit ( atom , ion , molecule ) in a crystal (e.g. ion crystal , metal lattice ) or the number of atoms directly bound to a central atom in a complex . A crystal structure is defined by specifying the position of its building blocks; H. by their coordination in the unit cell .
The coordination numbers 4 and 6 occur most frequently, with 2, 3, 8 and 12 also occurring, and sometimes other values in complexes. The coordination number depends , among other things, on the radius ratio of the ions (in the ion crystal ) or on the binding properties (in complexes ). The coordination number in crystals usually increases with pressure, e.g. B. the transition from graphite (KZ: 3) to diamond (KZ: 4).
The coordination number in crystal lattices is given in square brackets. Table salt is an example : Na [6] Cl [6], which corresponds to a rectangular lattice structure. Every sodium ion has 6 neighboring chloride ions and every chloride ion has 6 neighboring sodium ions; the coordination polyhedron in both cases is an octahedron .
In certain crystal structures , the same structural unit can also occur in positions with different coordination numbers.
Examples
The following table shows the coordination numbers for some types of grids.
| Lattice structure | Coordination number |
|---|---|
| simple cubic ( sc ) | 6th |
| face-centered cubic ( fcc ) | 12 |
| body-centered cubic ( bcc ) | 8th |
| hexagonal close packing of spheres ( hcp ) | 12 |
| Diamond structure | 4th |
literature
- R. Hoppe: The coordination number - an "inorganic chameleon" . In: Angewandte Chemie , 82 (1), 1970, pp. 7-16, doi: 10.1002 / anie.19700820103
Individual evidence
- ^ Harald Ibach, Hans Lüth: Solid State Physics . 7th edition. Springer Verlag, Berlin 2009, ISBN 978-3-540-85794-5 , pp. 31-35 .