Alcian blue
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
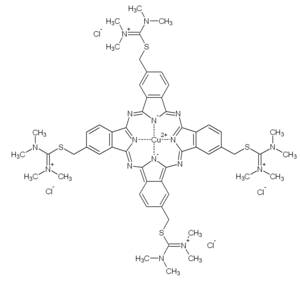
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Alcian blue | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 56 H 68 Cl 4 CuN 16 S 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
blue solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 1298.86 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
1 g l −1 in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Alcian blue is a dye used in histology to selectively stain mucus-producing tumors, acid mucins, and sulfated glycosaminoglycans (such as hyaluronic acid or chondroitin sulfate ) cyan at low pH (1.0 to 2.5).
properties
Due to the isothiouronium groups in solution, Alcian blue is unstable at a higher pH value and room temperature, while the water-insoluble product phthalocyanine blue , which is created by washing at a neutral or basic pH value , is stable.
The absorption maximum of Alcian blue is 600 to 610 nm (Alcian blue aggregates), in addition the rarer monomeric form has an absorption maximum at 670 to 680 nm. Alcian blue also colors suramin . With increasing ionic strength , coloring with Alcian blue is prevented, which means that a characteristic salt concentration ( critical electrolyte concentration , CEC) can be determined from which coloring no longer takes place. Mixing Alcian blue with Alcian yellow creates Alcian green .
use

In histology, the derivative Alcian blue 8G (formerly 8GX) is mainly used for Alcian blue staining .
Alcian blue is also used as a cationic-aromatic adhesive for attaching thin sections embedded in glycol methacrylate . Alcian blue binds to cell membranes and can also be used to coat cells in preparation for electron microscopy , after removing the dye layer ( unroofing , roofing), the inside of the cell membrane can be viewed on it. Alcian blue can also be used as a substitute for polylysine for coating cell culture bottles for adherent cells.
history
Alcian blue is a derivative of copper phthalocyanine and was developed in 1947 in the department of NH Haddock and C. Wood of Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) as Ingrain blue 1 (English for 'blue precipitate dye 1'). The aim of Ingrain dyes was with easily removable stable textile dye hydrophilic produce isothiouronium groups. After binding to the textile fibers, the hydrophilic groups would be removed, making the dye water-insoluble and precipitating on the textile fiber. Alcian blue was originally used as a textile dye . It was introduced into histology in 1950 by Harold F. Steedman as the "mucus dye". It has become one of the most important dyes in histology. The structure of Alcian blue was published in 1972 and confirmed by ICI in 1973 when production ceased there.
literature
- JE Scott: Alcian blue. Now you see it, now you don't. In: European journal of oral sciences. Volume 104, Number 1, February 1996, pp. 2-9. PMID 8653492 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Alcian Blue 8GX, powder from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on March 13, 2016 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Data sheet of the pathology of the University of Erfurt, (PDF)
- ↑ a b c d John D. Bancroft: Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2008, ISBN 978-0-443-10279-0 , p. 172.
- ^ W. Dong, YK Matsuno, A. Kameyama: A procedure for Alcian blue staining of mucins on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. In: Analytical chemistry. Volume 84, Number 20, October 2012, pp. 8461-8466, doi: 10.1021 / ac301678z . PMID 22950532 .
- ↑ University of Zurich: Histology course, (online)
- ↑ Pathology Institute of the LMU: Histological staining, (online)
- ↑ Data sheet ALCIANBLAU 8 GS (CI 74240) (PDF) from Carl Roth , accessed on March 13, 2016.
- ↑ Jürgen Bruns: Tissue Engineering News on tissue replacement in the musculoskeletal system . Springer-Verlag, 2011, ISBN 978-3-642-57353-8 , pp. 68 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ a b c d e M.A. Hayat: Stains and Cytochemical Methods . Springer Science & Business Media, 1993, ISBN 978-0-306-44294-0 , pp. 80 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ JA Kiernan: Dyes and other colorants in microtechnique and biomedical research. In: Coloration Technology . 122, 2006, p. 1, doi: 10.1111 / j.1478-4408.2006.00009.x .
- ↑ RW Horobin, DJ Goldstein: Impurities and staining characteristics of Alcian Blue samples. In: The Histochemical Journal. (1972), Volume 4, Issue 5, pp. 391-399, doi: 10.1007 / BF01012530 .
- ↑ Eric Archimbaud, Anwarul Islam, Harvey D. Preisler: Alcian Blue Method for Attaching Glycol Methacrylate Bone Marrow Sections to Glass Slides. In: Stain Technology. 61, 2009, p. 121, doi: 10.3109 / 10520298609110719 .
- ^ Academic Press: Introduction to Electron Microscopy for Biologists. Academic Press, 2008, ISBN 978-0-08-088816-3 .
- ↑ W. Mohr: Pathology of the ligament apparatus tendons · tendon sheaths · fascia · bursa . Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-72843-3 , p. 37 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ HF Steedman: Alcian Blue 8GS: A New Stain for Mucin . In: Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science . tape 91 , 1950, pp. 477-479 , PMID 24540170 ( PDF ).
- ↑ JE Scott: Alcian dyes: ICI cease manufacture and release details of composition. In: Histochemistry and Cell Biology. (1973) Volume 37, Number 4, pp. 379-380.