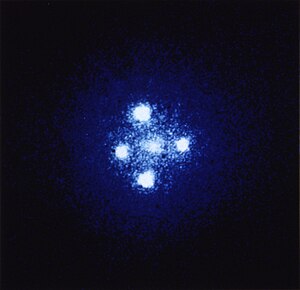
Einstein Cross
| Einstein Cross / Huchras Lens | |
|---|---|
|
Observation dates equinox : J2000.0 , epoch : J2000.0 |
|
| Constellation | Pegasus |
| Right ascension | 22 h 40 m 30.3 s |
| declination | + 3 ° 21 ′ 31 ″ |
| Gravitational lens: Huchra's lens | |
| Type | Galaxy |
| Brightness (V-band) | 16.8 likes |
| Angular expansion | 0.87 ′ × 0.34 ′ |
| Redshift | 0.039 |
| distance | 400 million light years |
| Catalog names | CGCG 2237 + 0305 • PGC 69457 |
| Depicted object: Einstein Cross | |
| Type | quasar |
| Angular expansion | 1.6 "x 1.6" |
| Brightness (V-band) | (A) 17.4 mag; (B) 17.4 mag (C) 18.4 mag; (D) 18.7 mag |
| Redshift | 1.695 |
| distance | about 8 billion light years |
| Catalog names | QSO B2237 + 030 • QSO B2237 + 0305 • QSO J2240 + 0321 |
| history | |
| Explorer | John Huchra |
| discovery | 1985 |
The Einstein Cross, also Q2237 + 030 or QSO 2237 + 0305, is a gravitational lens system in the constellation Pegasus . The quasar QSO 2237 + 0305 is from Earth seen just behind the core of about 400 million light-years distant galaxy acting as a gravitational lens and as Huchras lens is known (after its discoverer John Huchra ). The gravitational lens creates four similarly bright images in the form of a cross with the galaxy core in the center. The quasar pictured is about eight billion light-years from Earth . The opposite images of the quasar in the Einstein Cross have an apparent distance ( Einstein radius ) of 1.6 arc seconds .
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b SIMBAD
- ↑ a b c d NASA and ESA: The Gravitational Lens G2237 + 0305 . In: HubbleSite . September 13, 1990 . Retrieved July 25, 2006.
Web links
- Skyhound.com about Einsteinkreuz (English)
- Astronomy-Mall.com about the gravitational lens (English)
- Jay Reynolds Freeman about the Quasar (English)
- The Einstein Cross Gravitational Lens - Astronomy Picture of the Day of March 11, 2007 (English).
- Simbad