Euhelopus
| Euhelopus | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
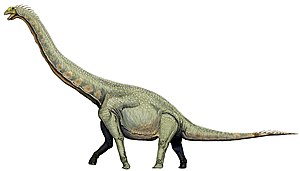
Live reconstruction of Euhelopus zdanskyi |
||||||||||||
| Temporal occurrence | ||||||||||||
| Lower Cretaceous ( Barremium to Albium ) | ||||||||||||
| 130 to 112 million years | ||||||||||||
| Locations | ||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Euhelopus | ||||||||||||
| Wiman , 1929 | ||||||||||||
| Art | ||||||||||||
|
Euhelopus ( "good mud-feet" ) was a sauropod dinosaur , which wasdiscovered and describedby Carl Wiman in1929 in the Meng-Yin Formation in the Chinese province of Shandong . It lived in the Lower Cretaceous about 130 to 112 million years ago and could reach a length of about 15 meters. The weight was estimated to be more than 15 tons. Regarding the system , Euhelopus is counted amongthe Titanosauria . This group is mainly represented by massive sauropods. So faronly one species of this genus is known, Euhelopus zdanskyi . The front extremities, which are longer than the rear ones, arespecial on the physique of Euhelopus . Otherwise, its appearance resembles that of other sauropods, so it had a long neck and tail, a massive body supported by four sturdy legs, and a small skull. Euhelopus was herbivorous (fed on plants).
Originally this dinosaur was named Helopus by Wiman . However, a bird already had this name. Accordingly, in 1956 the name Helopus was changed from Alfred Romer to Euhelopus . There is also a species of plant called Helopus , but this is only possible because plants and birds are in two different realms .
So far no complete skeleton of Euhelopus has been recovered. For the most part, fragments of cervical vertebrae and the spine and a toothless skull have been discovered. These fossil finds are now in the Paleontological Museum of Uppsala University , Sweden .
swell
Individual evidence
- ↑ Jeffrey A. Wilson, Paul Upchurch : Redescription and reassessment of the phylogenetic affinities of euhelopus zdanskyi (Dinosauria: Sauropoda) from the early cretaceous of China. In: Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. Vol. 7, No. 2, 2009, ISSN 1477-2019 , pp. 199-239, doi : 10.1017 / S1477201908002691 .
- ↑ Data on Euhelopus ( memento from January 2, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) - location ( memento from January 3, 2007 in the Internet Archive ), accessed on August 14, 2014.
- ↑ Euhelopus on the homepage of the paleontological museum Uppsala ( Swedish ), accessed on August 14, 2014.
Web links
- Euhelopus ( Memento from September 22, 2009 in the Internet Archive ), accessed on August 14, 2014.
- Euholepus on Dinosaurier-Info.de , accessed on August 14, 2014.
- Posture of the neck of Euhelopus , accessed on August 14, 2014.