European paddock toads
| European paddock toads | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Common spadefoot toad ( Pelobates fuscus ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the family | ||||||||||||
| Pelobatidae | ||||||||||||
| Bonaparte , 1850 | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the genus | ||||||||||||
| Pelobates | ||||||||||||
| Wagler , 1830 |
The European spadefoot ( Pelobates ), also European blade toads called, are the only genus within the same family. The family's scientific name is Pelobatidae .
features
European paddock toads are moderately large, stocky frogs with smooth skin. Adult specimens reach a head-trunk length of 50 to 100 mm. Their legs are short and the webbed toes are well developed. The pupils are vertically slit-shaped. It is named after the keratinized heel hump on the hind feet , which serves as a "grave shovel" .
The mouth areas of the tadpoles are keratinized (keratinized). Your left and right branchial chambers merge behind the heart and are emptied through a breathing hole on the left side in the middle of the body.
distribution
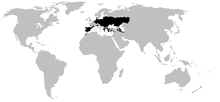
The range of the European paddock toads includes western Europe, north-western Africa and western Asia. Of the four species, only the potentially endangered knife foot ( Pelobates cultripes ) occurs exclusively in Europe. The endangered Moroccan knife foot ( Pelobates varaldii ) lives exclusively in fragmented habitats in the coastal plains of Morocco .
Way of life
European paddock toads spend much of their life in self-dug burrows. With the help of sharp-edged "digging shovels" on the hind feet, they dig into the ground, whereby the hind legs are moved alternately. They prefer open habitats with loosely grounded habitats, but can also be found in cultivated landscapes . The reproduction takes place explosively, i.e. in short, simultaneous activity, during which they migrate into the waters in spring. The males do not have a vocal sac and give deep cries underwater. The amplexus during mating occurs in the groin area of the female, 3500 to 7000 eggs are laid in long spawning cords . The tadpole stage lasts in the Syrian shovel toad 2 to 3 months, in the spadefoot it takes longer and the larvae can overwinter up to 3 years depending on the climate. 1 With a total length of 180 mm, the long larval stage results in the longest tadpoles of all European frogs .
Systematics
The German-language name European sea-toed toads mainly serves to distinguish it from the family of American sea-toed toads , with which they formerly formed a common family. However, they are more closely related to the Asian toad frogs , together with which they were placed in the superfamily toad frogs (Pelobatoidea).
species
The European paddock toad family includes five species:
-
Pelobatidae
Bonaparte , 1850
-
Pelobates Wagler , 1830
- Knife foot - Pelobates cultripes ( Cuvier , 1829)
- Common Garlic Toad - Pelobates fuscus ( Laurenti , 1768)
- Syrian common toad - Pelobates syriacus Boettger , 1889
- Moroccan knife foot - Pelobates varaldii Pasteur & Bons , 1959
- Eastern Common Toad - Pelobates vespertinus Pallas , 1771
-
Pelobates Wagler , 1830
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Laurie J. Vitt, Janalee P. Caldwell: Herpetology: An Introductory Biology of Amphibians and Reptiles. 2013, Elsevier Ltd, ISBN 978-0123869197 , p. 479.
- ↑ Description and species list of the family Pelobatidae in Amphibiaweb
- ↑ Pelobates cultripes in the IUCN 2017-3 Red List of Threatened Species . Posted by: Beja et al. , 2008. Retrieved December 17, 2017.
- ↑ Pelobates varaldii in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017-3. Posted by: Alfredo Salvador et al. , 2006. Retrieved December 17, 2017.
Web links
- Darrel R. Frost: Pelobates Wagler, 1830 . In: Amphibian Species of the World: an Online Reference. Version 6.0. American Museum of Natural History, New York 2016, accessed June 10, 2016