Fluorobenzoic acids
| Fluorobenzoic acids | |||||||
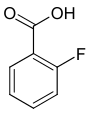
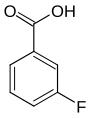
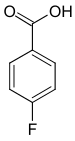
| Surname | 2-fluorobenzoic acid | 3-fluorobenzoic acid | 4-fluorobenzoic acid | ||||
| other names | o -fluorobenzoic acid | m -fluorobenzoic acid | p -fluorobenzoic acid | ||||
| Structural formula |
|
|
|
||||
| CAS number | 445-29-4 | 455-38-9 | 456-22-4 | ||||
| PubChem | 9935 | 9968 | 9973 | ||||
| Molecular formula | C 7 H 5 FO 2 | ||||||
| Molar mass | 140.12 g mol −1 | ||||||
| Physical state | firmly | ||||||
| Brief description | white, crystalline solids | ||||||
| Melting point | 122-125 ° C | 122-124 ° C | 182-184 ° C | ||||
| pK s value | 3.27 | 3.90 | 4.14 | ||||
|
GHS labeling |
|
|
|
||||
| H and P phrases | 315-335 | 315-335 | 302-318 | ||||
| no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | no EUH phrases | |||||
| 261 | 261 | 280-305 + 351 + 338 | |||||
The fluorobenzoic acids (FBAs) form a group of substances in chemistry that is derived from both benzoic acid and fluorobenzene . The structure consists of a benzene ring with an attached carboxy group (–COOH) and fluorine (–F) as substituents . Their different arrangement results in three constitutional isomers with the empirical formula C 7 H 5 FO 2 .
The fluorobenzoic acid group also includes multiple fluorine-substituted benzoic acids (e.g. 2,3-DiFBA, 2,3,4-TriFBA, 2,3,4,5,6-PentaFBA ...), which have a large number of isomers allow very similar physical properties.
presentation
The synthesis succeeds by means of the Schiemann reaction by diazotization of the aminobenzoic acids . The diazonium salt is precipitated as tetrafluoroborate by adding tetrafluoroboric acid (HBF 4 ) and then carefully heated.
properties
The fluorobenzoic acids are white, crystalline solids. The melting points of 2- and 3-fluorobenzoic acid hardly differ. The 4-fluorobenzoic acid has a significantly higher melting point, since particularly strong intermolecular hydrogen bonds occur due to the higher symmetry . The fluorobenzoic acids have a higher acidity compared to benzoic acid due to the −I effect of the fluorine substituent. The pK s values are therefore correspondingly lower (benzoic acid: 4.20).
2-Fluorobenzoic acid is metabolized to catechol by Pseudomonad . 4-fluorobenzoic acid is produced by Pseudomonas sp. B13 completely metabolized.
use
FBAs are used as tracers in hydrogeology . Their use is used to clarify the flow paths of groundwater, the seepage behavior of precipitation in the ground and the connection between oil reservoirs. The use of fluorobenzoic acids is also being examined in connection with CO 2 sequestration in saline aquifers. They could be used here for leak monitoring of the underground reservoir. In the event of a leak, traces of FBAs would be detectable in the groundwater.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Data sheet 2-Fluorobenzoic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 29, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Data sheet 3-Fluorobenzoic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 29, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b Data sheet 4-Fluorobenzoic acid from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 29, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ a b CRC Handbook of Tables for Organic Compound Identification , Third Edition, 1984, ISBN 0-8493-0303-6 .
- ^ K. Peter C. Vollhardt , Neil E. Schore: Organische Chemie , 4th edition, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2005, ISBN 978-3-527-31380-8 , p. 1193.
- ^ GWA Milne, Peter Goldman, Jordan L. Holtzman: "The Metabolism of 2-Fluorobenzoic Acid", in: Journal of Biological Chemistry , 1968 , 243 (20), pp. 5374-5376; Abstract ; PDF; 272 kB .
- ↑ A. Schreiber, M. Hellwig, E. Dorn, W. Reineke, H.-J. Knackmuss: "Critical Reactions in Fluorobenzoic Acid Degradation by Pseudomonas sp. B13", in: Appl. Environ. Microbiol. , 1980 , 39 (1), pp. 58-67; PMC 291284 (free full text).
- ^ Q. Hu, JE Moran: "Simultaneous analyzes and applications of multiple fluorobenzoate and halide tracers in hydrologic studies", in: Hydr. Proc. , 2005 , 19 , pp. 2671-2687.
- ↑ Th. Gieles, H.-C. Beuthan: "Use of tracers in petroleum fields", in: Erdgas Erdöl Kohlen , 2004 , 120 , pp. 26-29.
literature
- J. Krausse and H. Dunken: "The crystal and molecular structure of o -fluorobenzoic acid", in: Acta Cryst. , 1966 , 20 , pp. 67-73; doi : 10.1107 / S0365110X66000124 .
- Karsten Müller: "Detection of fluorobenzoic acids using IC-UV / Vis and GC-MS" , diploma thesis, Marburg 2008 (PDF file; 15.2 MB).

